There are a lot of different ways to create a plastic part, but some methods get grouped together, whether it’s because the parts they can make are similar, their processes work in a similar way, or because they are good alternatives for one another. In the world of plastic design, injection molding often gets weighed up against thermoforming.
While you can draw a few similarities between the two, each has its differences and reasons for why you’d want to make a product with thermoforming versus injection molding. We’re going to look at how each works and where their strengths and weaknesses lie.
Injection Molding Definition and Comparison to Thermoforming
One way you can go about making a plastic part is through a process called injection molding, which relies on a specialized machine to form molten material inside molds with multiple cavities. It works by pouring plastic pellets into an injection barrel, which will then get heated until molten. Once it reaches this ultra-hot temperature, the liquid mixture gets funneled into the molds, where pressure forms it into tight shapes, and then it will cool.
Once the products are cool, they’ll be removed and sent on to whatever future they have in store. Initially, this kind of manufacturing process was made to create small things like combs and buttons, but now it’s an enormously popular choice for a large range of items. It’s also super cost-effective when it comes to large production orders.
In the diagram below, you can see each part of an injection molding machine.
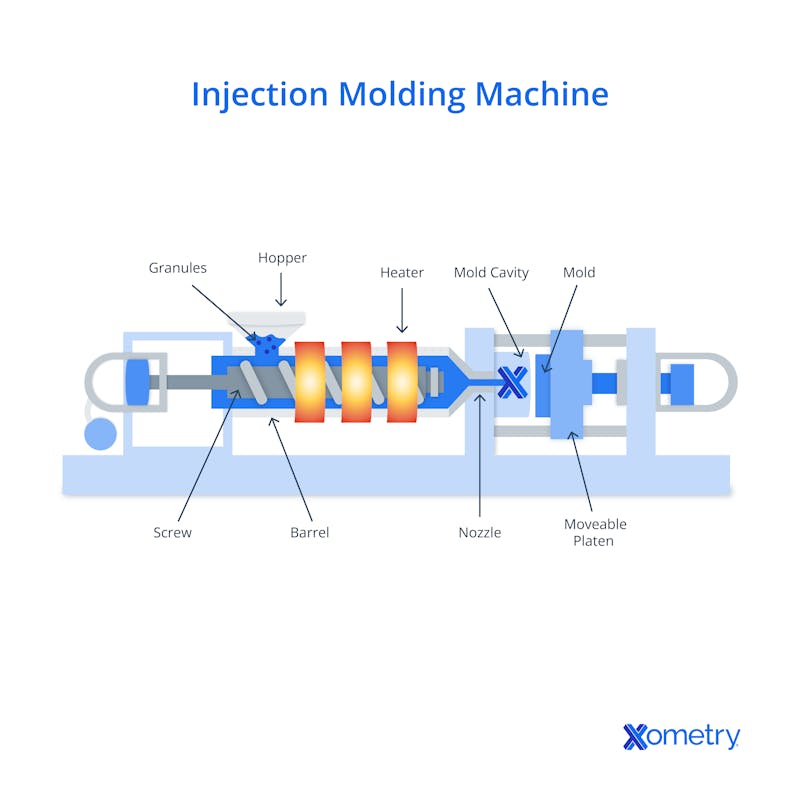
What are the Advantages of Injection Molding Compared to Thermoforming?
Listed below are some advantages of injection molding compared to thermoforming:
- Ideal for high-volume production since injection molds can have several cavities
- Great for producing small and/or intricate parts.
- Adaptable to a high level of automation for high-volume production.
What are the Disadvantages of Injection Molding Compared to Thermoforming?
Listed below are the disadvantages of injection molding compared to thermoforming:
- High tooling and equipment costs can be a barrier to entry for some companies wishing to use injection molding.
- Long lead times for mold building and repair due to the complexities of the shapes typically being molded.
Thermoforming Definition and Comparison to Injection Molding
Rather than pellets, this kind of plastic manufacturing technique uses sheets that are pressed into a single-sided mold to create products. These machines also use pressure to ensure the sheet fills out every bit of the mold, and vacuum forming, in particular, makes sure there are no trapped air bubbles.
Thermoforming started out by using cellulose sheets to create harder materials, and nowadays it’s a go-to choice for everything from large-scale products (like bathtubs) to smaller containers and toys.
You can see a diagram of a thermoforming machine below and what the process looks like.
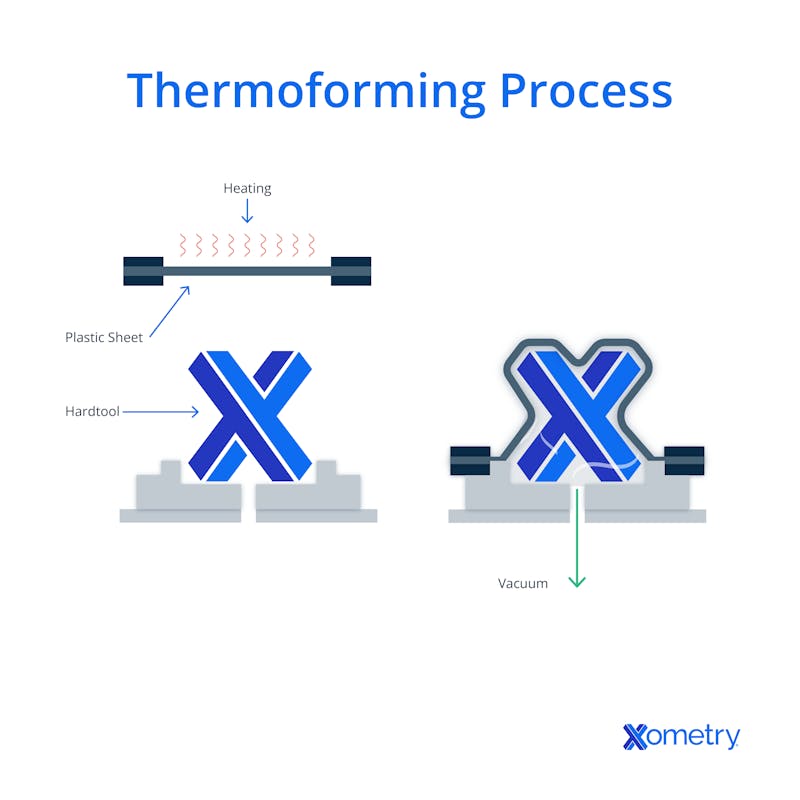
What are the Advantages of Thermoforming Compared to Injection Molding?
Listed below are the advantages of thermoforming compared to injection molding:
- Great for low-volume production runs or one-offs, since only one part can be made at a time
- Faster prototyping and product development, since it is easier to make thermoforming tooling than injection molding tooling
- Low tooling costs, since thermoforming tools, are typically made from aluminum
- Easy to make repairs and modifications to tooling, since thermoforming tooling is relatively simple
What are the Disadvantages of Thermoforming Compared to Injection Molding?
Listed below are the disadvantages of thermoforming compared to injection molding:
- Unsuitable for high-volume production, since production output is low with thermoforming
- Labor-intensive, since some thermoformed parts must be post-processed to meet customer specifications.
- Wasteful, because correctly thermoformed parts may require several attempts before they attain the desired shape.
Comparison Table Between Injection Molding and Thermoforming
The following table gives you a look at how injection molding and thermoforming compare.
| Attribute | Injection Molding | Thermoforming |
|---|---|---|
Attribute Can you have high-volume production | Injection Molding Yes | Thermoforming No |
Attribute Can make small detailed parts? | Injection Molding Yes | Thermoforming No |
Attribute Can make large parts with big tolerances? | Injection Molding No | Thermoforming Yes |
Attribute Does it have low tooling costs | Injection Molding No | Thermoforming Yes |
Attribute Are processes repeatable? | Injection Molding Yes | Thermoforming Yes |
Attribute Applications | Injection Molding Gears, bottle caps, packaging, one-piece furniture, toys, bottles, consumer electronics | Thermoforming Toys, bathtubs, bottles, agricultural products, appliances, light fixtures, trays, instrument panels, displays, food containers, ducts, windshields for boats |
Attribute Waste levels | Injection Molding Minimal waste | Thermoforming Pretty wasteful since incorrect parts will have to be redone and may take several rounds |
Attribute Materials | Injection Molding Various plastics in pellet format (polyethylene, polycarbonate, and PVC as examples) | Thermoforming Various plastics in sheet format (polyethylene, polycarbonate, and PVC as examples) |
Attribute Production speed | Injection Molding Capable of rapid production | Thermoforming Capable of rapid production (final product design is faster because it’s easier to change the tooling with thermoforming) |
Attribute Volume | Injection Molding Higher production volume than thermoforming, especially with molds that have more cavities | Thermoforming One part per molding cycle |
Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming Attributes
Deciding whether injection molding vs. thermoforming is right for a project comes down to the specific requirements. If high-volume production is required or the application is a small, complex part, injection molding is better. If larger parts at low-volume production are needed, thermoforming is better.
Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming: Lead Cost Comparison
Tooling costs for thermoforming can be significantly less than for injection molding. Because pressures used in thermoforming are not as high as injection molding, most thermoforming tooling is made from aluminum. Compare that to the injection molding process, which uses expensive tool steels such as P20 or H13. Fabricating tooling for injection molding can take a long time and may be much more labor-intensive than thermoforming molds due to the complexity of the parts being molded.
Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming: Speed Comparison
Both injection molding and thermoforming are excellent at producing parts at a rapid pace. The main difference is that with injection molding, molds can sometimes have multiple cavities fed by the same supply of molten material, leading to much higher output. The development of final product design and molds is faster with thermoforming because the tooling can be easily modified.
Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming: Volume Comparison
Injection molding can support much higher production volumes than thermoforming. This is because injection molds can have multiple cavities. Some molds can have over 100 cavities. In the thermoforming process, on the other hand, just a single part is made during every molding cycle. As a result, injection molding is much better for large or frequent production orders.
Injection Molding vs. Thermoforming: Materials Comparison
Injection molding and thermoforming can generally use the same plastic materials, such as polyethylene, polycarbonate, and PVC. Because injection molding uses plastic pellets and thermoforming uses plastic sheets, the materials used in thermoforming generally have more malleable and ductile characteristics.
Frequently Asked Questions About Injection Molding and Thermoforming
What are the Mutual Alternatives to Injection Molding and Thermoforming?
Blow molding and extrusion molding are great alternatives if you’re after a replacement for the likes of injection molding and thermoforming. They can also whip up plastic products in large quantities, and you can repeat the process with ease. Blow molding is superb for containers and bottles, whereas extrusion molding is a good choice if you’re after weather seals, pipes, and door frames, which are easily made with extrusion molding.
What are the Similarities Between Injection Molding and Thermoforming?
Injection molding and thermoforming have quite a lot of differences, but you’ll find they’re similar in two main ways—they both use thermoplastics, and you can repeat processes without too much struggle when you’re making high-quality parts.
Is injection molding or thermoforming more expensive?
Injection molding tends to be more expensive than thermoforming. That’s because thermoforming has lower tooling costs and cheaper parts since it won’t experience the same pressure levels as injection molds. Injection molding machines need components made of quality materials like P20 or H13 steel, and tooling can be more complex.
What are the Other Comparisons for Injection Molding Besides Thermoforming?
Listed below is another alternative to injection molding:
- Injection Molding vs. 3D Printing: 3D printing is a fabrication process that can create parts with complex geometry with ease, as injection molding does. Some complex-geometry parts cannot be made with injection molding due to undercuts and other unmoldable features. 3D printing avoids this problem and can print any part, no matter the complexity, with both ease and speed.
What are the Other Comparisons for Thermoforming Besides Injection Molding?
Listed below is another alternative to thermoforming:
- Thermoforming vs. Blow Molding: While thermoforming can only be used to make one half of an assembly at a time, blow molding can make both halves of a hollow container in one cycle. Items such as bottles, containers, and other items can easily be made with blow molding.
How Xometry Can Help
Producing plastic parts is more than possible at Xometry, and we have a long list of manufacturing services you can get instant quotes for depending on your needs, including for plastic injection molding and customized services like thermoforming. Take a look at our plastic 3D printing, plastic extrusion, custom thermoforming and plastic laser cutting pages for more information.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


