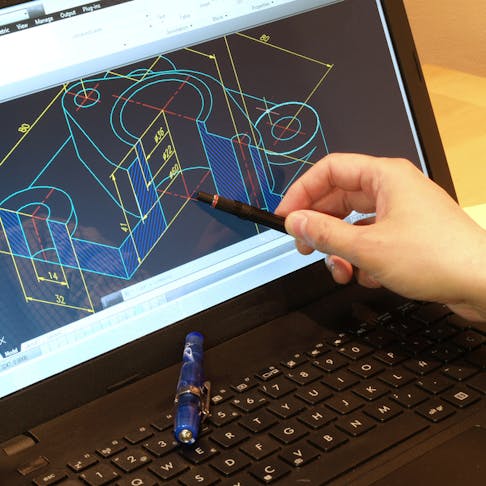
Computer-aided design (CAD) modeling revolutionizes the way products are designed and engineered by employing software to create precise digital representations. CAD enables designers to conceptualize, visualize, and analyze complex designs before production, streamlining the entire development process.
A variety of CAD modeling techniques exist, each suited to particular design specifications and industry verticals. These include: 2D drawing, 3D modeling, parametric modeling, and surface modeling. CAD software is used by automotive experts to design complex car components, while architectural firms use it to create precise building blueprints. It is imperative in today's digitally-driven design environment to comprehend CAD modeling and its various applications. Within the article, we'll delve deeply into every kind of CAD modeling, including illustrations and perspectives on how they're used in many sectors.
What Is CAD Modeling?
CAD modeling refers to the process of creating digital representations of real-world objects or systems using computer-aided design (CAD) software. These models can be 2D or 3D and are characterized by their precision, scale, and physical properties. CAD models enable engineers and designers to visualize, analyze, and optimize designs before manufacturing, leading to more efficient and accurate product development processes.
How Has CAD Modeling Evolved Over the Years?
CAD modeling has progressed from simple 2D programs like ADAM™ and Sketchpad to complex 3D programs like ANVIL-4000® and Unigraphics. Technologies such as ANVIL-4000® enhanced capability with geometry control, drafting, and analysis modules, while innovations like Sketchpad III added 3D capabilities. The widespread use of 3D modeling in CAD is a result of this progress, which was driven by industry contributions and research at universities like MIT.
How Does CAD Work?
CAD (computer-aided design) works by allowing users to create, modify, and analyze digital models of physical objects. It uses geometric shapes, dimensions, and constraints to represent the object's structure and behavior. CAD software provides tools for: drawing, editing, and visualizing designs in 2D or 3D. Users can input precise measurements, apply materials and textures, and simulate real-world conditions. Ultimately, CAD streamlines the design process, facilitates collaboration, and improves accuracy in engineering and manufacturing.
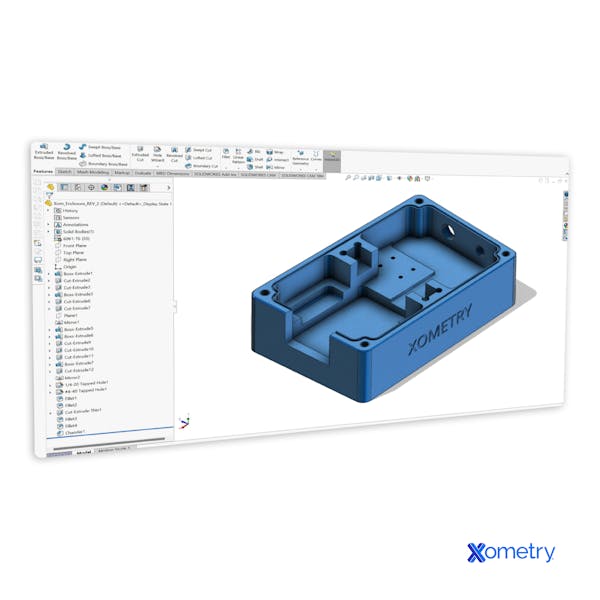
An example CAD modeling.
What Is the Purpose of CAD?
The goal of computer-aided design (CAD) is to replace manual drafting techniques with a more efficient way to create accurate and detailed design representations. Engineers may create, edit, and refine designs digitally with CAD, which improves process accuracy and productivity. CAD software may also compute how various materials interact with one another in a design.
What Are the Types of CAD?
The types of CAD include:
1. 2D CAD
2D CAD, or two-dimensional computer-aided design, is a software tool used to create digital representations of objects or systems in flat drawings. It employs fundamental geometric shapes like: lines, rectangles, and circles to depict designs. 2D CAD is utilized for: drafting, planning, and detailing structures in various industries. It offers features such as: text annotations, dimensions, and tables, enabling precise documentation and communication of design concepts.
2. 3D CAD
3D CAD software, in contrast to its 2D equivalent, enables users to produce three-dimensional digital models with depth and volume, which gives designs life. As a result, it lets designers control items in a virtual 3D world, this kind of CAD is invaluable in: engineering, product design, and visualization. Precise representation of complicated geometries and minute features is possible with 3D computer-aided design (CAD), which improves design concept analysis, visualization, and communication.
3. Parametric CAD
Parametric CAD, or parametric computer-aided design, is a design approach in which models are created based on defined parameters and relationships between them. Designers use parameters to represent dimensions, angles, and other features, adding constraints to maintain relationships within the model. This method enables easy modification and adaptation of designs, offering flexibility and control over various design elements.
4. Direct Modeling CAD
Direct Modeling CAD software offers a more flexible approach to design, allowing users to manipulate geometry directly, without the need for predefined parameters or constraints. With direct modeling, designers can easily make quick modifications to their designs, exploring different iterations and variations on the fly. Designers may quickly experiment with different iterations and variants of their designs by modifying them with direct modeling. This kind of CAD is very helpful for rapid prototyping and idea modeling, in which it's critical to iterate designs quickly and nimbly.
5. Surface Modeling CAD
Surface Modeling CAD software specializes in creating digital models by defining and manipulating surfaces rather than solid volumes. It is commonly used in industries such as automotive and aerospace engineering, in which complex curves and freeform shapes are prevalent. Surface modeling allows designers to create aesthetically pleasing and aerodynamically efficient designs, offering greater flexibility and precision in modeling organic shapes and surfaces.
6. 3D Wireframe CAD
3D Schematic computer-aided design, or CAD, is a method used to depict objects using lines, arcs, and curves to define an object's borders and depth. Basic geometric representations of objects are made with it, giving additional modeling a visual foundation. Wireframe CAD is more straightforward and uncomplicated than solid or surface modeling; yet, it is devoid of realistic rendering capabilities and comprehensive surface information.
7. Solid Modeling CAD
Solid Modeling CAD software focuses on creating digital models with defined volumes and shapes, representing objects as solid entities. This type of CAD is widely used in industries such as manufacturing and mechanical engineering, in which precise geometric representations are essential. Solid modeling enables designers to create detailed and accurate models, incorporating features such as fillets, chamfers, and blends to enhance realism and functionality.
8. Freeform or Sculpting CAD
Freeform or Sculpting CAD software empowers designers to create organic shapes and complex surfaces with unparalleled freedom and creativity. Unlike traditional CAD techniques that rely on geometric primitives, freeform modeling allows for intuitive sculpting and shaping of digital clay-like forms. This kind of computer-aided design (CAD) is widely utilized in fields including character modeling, industrial design, and artistic visualization. It provides a flexible set of tools for exploring ideas and expressing creativity.
9. BIM (Building Information Modeling)
Building Information Modeling (BIM) software revolutionizes the architectural and construction industries by integrating design, documentation, and collaboration into a single platform. BIM software allows architects, engineers, and contractors to create and manage digital representations of building projects, incorporating information such as: materials, structures, and spatial relationships. BIM enables stakeholders to visualize, simulate, and analyze building designs, improving coordination, efficiency, and sustainability throughout the construction life cycle.
10. 2D/3D Hybrid CAD
2D/3D hybrid CAD software offers workflow flexibility and diversity by combining the strengths of 2D and 3D modeling methodologies. By using a hybrid technique, users may take advantage of 3D modeling's strength for visualization and analysis, as well as the accuracy and ease of 2D drafting for thorough documentation and annotation. For businesses like architecture, in which both 2D drawings and 3D models are necessary for efficient communication and decision-making, this kind of computer-aided design is perfect.
3D CAD in a solid file format is one of the best ways to share technical information with your manufacturer. Xometry can take most native CAD files, but when in doubt use a STEP file as it's like the PDF of the CAD world and is universally accepted.Greg PaulsenDirector, Applications Engineering
Who Uses CAD?
CAD is utilized by a diverse range of professionals across various industries, including: engineers, architects, product designers, interior designers, and manufacturers. These individuals leverage CAD software to create precise design drawings, models, and simulations. From conceptualization to prototyping and production, CAD is integral in streamlining the design process and ensuring accuracy and efficiency in bringing ideas to fruition.
How Is CAD Used With 3D Printers?
CAD plays a crucial role in the 3D printing process by offering the digital design files required for layer-by-layer printing of items. Using CAD software, designers produce 3D models that have precise dimensions, forms, and features. Then, these digital designs are exported in file formats that work with 3D printers, such as OBJ or STL. Production and prototyping may happen quickly because of CAD's precise and adaptable construction.
What Are the Examples of CAD Software?
Examples of CAD software include:
- Tinkercad®: A browser-based 3D modeling tool known for its simplicity and suitability for creating models for 3D printing, offering features for constructing complex models using constructive solid geometry.
- SolidWorks®: A parametric modeler from Dassault Systèmes, popular in mechanical engineering and design fields, offering tools for design validation and reverse engineering.
- FreeCAD: An open-source parametric modeler suitable for product design, mechanical engineering, and architecture, offering customization features and multi-platform support.
- Inventor®: CAD software from Autodesk® designed specifically for mechanical design, offering features for: 3D design, documentation, and product simulation, with tools for: sheet metal, frame, tube, and power design.
- AutoCAD®: Widely used CAD software from Autodesk® for 2D and 3D drafting and design, offering features for creating designs, equipment layouts, model documentation, and more.
What Are the Advantages of CAD Modeling?
The advantages of CAD modeling include:
- Precision: CAD modeling allows for precise and accurate design representation, ensuring that dimensions and properties are accurately captured and maintained throughout the design process.
- Efficiency: CAD modeling significantly reduces the time and effort required to create and modify designs compared to traditional manual drafting methods. Design iterations can be made quickly and easily.
- Visualization: CAD models provide realistic visual representations of designs in both 2D and 3D, allowing designers and stakeholders to visualize the final product before manufacturing.
- Collaboration: CAD modeling enables collaboration among designers, engineers, and other stakeholders by providing a platform for sharing and reviewing designs in real time, leading to better communication and decision-making.
- Simulation: CAD software often includes simulation tools that allow designers to test the performance and behavior of designs under various conditions, helping to identify potential issues and optimize designs before manufacturing.
What Are the Disadvantages of CAD Modeling?
The disadvantages of CAD modeling include:
- Initial Cost: Implementing CAD software and training personnel can involve significant up-front costs, especially for small businesses or individuals.
- Complexity: CAD software can be complex and require specialized training to use effectively, which may result in a steep learning curve for new users.
- Dependence on Technology: CAD modeling relies heavily on computer hardware and software, making it vulnerable to issues such as: system crashes, software bugs, and compatibility issues.
- Over-reliance on Automation: CAD software's automation features may lead to a loss of manual drafting skills and critical thinking abilities among designers, reducing their ability to solve complex design problems.
- Limited Physical Interaction: Unlike traditional manual drafting methods, CAD modeling does not provide physical interaction with design materials, making it difficult to assess tactile qualities such as texture and weight.
What Are Common Challenges Faced by CAD Modelers?
CAD modelers need a lot of training because they have to navigate complicated software. Data loss may occur while transferring models across software versions or systems due to compatibility problems. Software performance is impacted by hardware constraints such as sluggish processing speeds. These difficulties highlight the necessity of continual education, software upgrades, and hardware purchases to remove barriers and guarantee effective CAD modeling procedures.
What Are the Top Applications of CAD?
The top applications of CAD include:
- Product Design and Development: CAD software is extensively used in designing and developing various products across industries such as: automotive, aerospace, consumer goods, and electronics.
- Architectural Design: CAD enables architects to create detailed drawings and models of buildings, facilitating better visualization and communication with clients and construction teams.
- Engineering Analysis and Simulation: CAD allows engineers to analyze and simulate the performance of products and systems under different conditions, helping to optimize designs and identify potential issues.
- Civil and Infrastructure Projects: CAD is used in the design and planning of infrastructure projects like: roads, bridges, tunnels, and dams, enabling precise calculations and efficient resource utilization.
CAD is utilized by a diverse range of professionals across various industries, including: engineers, architects, product designers, interior designers, and manufacturers. These individuals leverage CAD software to create precise design drawings, models, and simulations. From conceptualization to prototyping and production, CAD is integral in streamlining the design process and ensuring accuracy and efficiency in bringing ideas to fruition.
Frequently Asked Questions About CAD Modeling
Are There Any Special CAD Tools Designed Specifically for Bioprinting?
Yes, there are CAD tools specifically designed for bioprinting. These tools integrate features tailored to the unique requirements of bioprinting processes, such as the ability to design complex 3D structures with intricate geometries while considering the biological properties of the materials being used. Some examples include Autodesk's® BioCAD and Mimics Innovation Suite (by Materialise) for Medical 3D Printing.
What Is the Difference Between CAD and Sketchup?
CAD (computer-aided design) software (such as AutoCAD®, etc.) is mostly used for accurate technical drawings and 3D modeling, which are often used in the fields of engineering, construction, and architecture. It provides cutting-edge tools for challenging tasks and needs unique to a given industry. On the other hand, SketchUp is more intuitive and adaptable, making it ideal for novices and enthusiasts. With capabilities like simple rendering and animation, it supports a variety of 3D modeling projects in addition to its focus on architectural design.
Summary
This article presented CAD modeling, explained it, and discussed its various types and examples. To learn more about CAD modeling, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including the ability to order 3D printed parts and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Copyright and Trademark Notices
- AutoCAD®, Autodesk®, Inventor®, and Tinkercad® are registered trademarks of Autodesk, Inc., and/or its subsidiaries and/or affiliates, in the United States.
- SolidWorks® is a registered trademark of Dassault Systèmes SolidWorks Corp.
- ANVIL-4000® is a registered trademark of Manufacturing and Consulting Services, Inc.
- ADAM™ is a trademark of Manufacturing and Consulting Services, Inc
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


