Large Scale 3D Printing Service on Xometry
Get instant online quotes on large scale 3D printed parts in dozens of plastic and metal materials. Free shipping on all US orders. ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, IATF 16949:2016, and AS9100D certified.
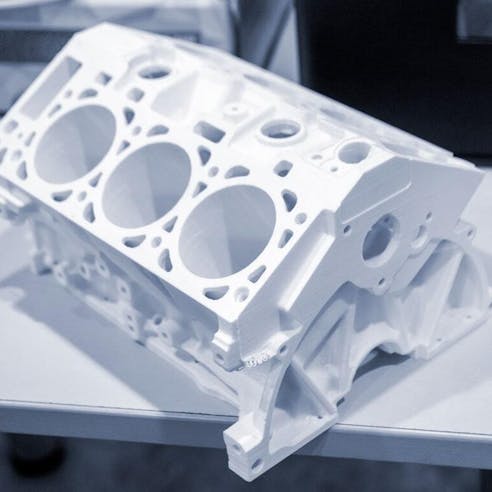
Xometry offers high quality Large Scale 3D Printing Services (also called Large Format 3D Printing). Xometry can provide single-print metal parts up to 9” (using DMLS) and single-print plastic parts up to 3’x2’x3’--however any part size can theoretically be achieved using part bonding.
The applications of large scale 3D printing is functionally endless, however its most common uses are for full-scale models, single print components, large prototypes, and other applications that would otherwise be laborious and expensive to produce with other manufacturing methods.
There are a variety of materials available for large scale 3D printing including both plastic and metal. Some of the common materials include ABS, PC, PLA, Aluminum, inconel, and many more.
Large format 3D printing with Xometry has a number of advantages, namely the ability to manufacture large parts with less material, energy, time, and labor costs. Large scale 3D printing also allows designers to create single components that would be difficult to produce using subtractive manufacturing methods in such large sizes. Large format 3D printing allows for better print quality and more resolution in details with much less direct operator involvement, creating a system that is both highly versatile and easy to deploy.
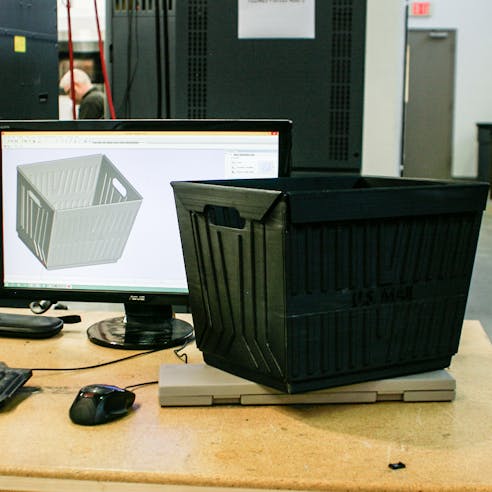

Large Format 3D Printing Part Sizes
| Material | Maximum Single Part Size | Maximum part size with part bonding |
|---|---|---|
Material Plastic | Maximum Single Part Size 3’x2’x3’ | Maximum part size with part bonding No upper bound (functionally infinite) |
Material Metal | Maximum Single Part Size up to 9” (DMLS) | Maximum part size with part bonding No upper bound (functionally infinite) |
Applications of Large Format 3D Printing
- Cost Reduction & Part Consolidation
- Large Scale Functional Prototyping
- Customized Manufacturing
Cost Reduction & Part Consolidation
In applications where costs are high, large scale 3D printing provides a fast, accurate, and highly repeatable process to both consolidate the part count and minimize manufacturing costs. Prior to large scale additive manufacturing, complex parts were either cast using die, sand, or investment casting or subtracted from larger stock, where both processes are time, labor, and money intensive. Not only this, but the needed casts, molds, patterns, cores, and other tooling for these processes require immense manufacturing effort to produce themselves. With large scale 3D printing, single parts can be made in a fraction of the time and the cost, and can reduce part count thanks to its increased print volume. Some modern applications that leverage part consolidation are low-volume production applications such as the aerospace and automotive industry using metals such as aluminum, steel, etc. or high-performance plastics. High volume production applications also benefit from large format 3D printing, as it can reduce fabrication and assembly costs by lowering the overall part count.
Large Scale Functional Prototyping
Most desktop 3D printers have smaller print volume ( around 12”x12”x12” with variation), restricting designers of large projects to either make scaled prototypes or print out and bond full scale parts together. With large scale additive manufacturing techniques, designers can prototype at full scale and can save on printing time, allowing designers to refine their prototypes faster and more accurately. Common materials for large-scale functional prototyping range from aesthetic plastics like ABS to economic plastics like PP or PE to performance plastics such as HDPE or metal-impregnated plastics.
Customized Manufacturing
When a product must be customized for its end-user, lead times are often long and costs are high. Due to the specific application of the design, many resources are spent refining the design and profit margins are limited to a single/low volume sale. With large scale additive manufacturing, designers can quickly produce parts that are customized exactly to the customer’s needs, and can reduce the labor and material costs associated with custom manufacturing. Common applications include those used in personalized applications such as medical and pharmaceutical industries using biocompatible materials like titanium, HDPE, ABS, etc.
Materials for Large Scale 3D Printing
Xometry offers large scale 3d printing in a range of materials, including: metal, plastics, resins, and specialty materials.
- Metal
- Plastics
- Resins
- Specialty Materials

Metal
Pure metals such as aluminum, titanium, etc. can be used in DMLS, SLS, and other powder bed fusion metal 3D printing tools to create full-metal parts, but alloys are the preferred choice for their enhanced material properties. Before use however, alloys must be vetted for their performance in laser-melting/sintering applications or manufacturers risk part failure. Commonly used alloys in metal 3D printing include tool steels, aluminum alloys, stainless steels, titanium alloys, and specialty alloys like Inconel and Cobalt-Chromium, and others. In DMLS, the maximum part size that can be printed is a 9”x9”x9” volume, however with parts bonding there is theoretically no maximum to part size. Common applications of 3D printed metal parts include aerospace, automotive, industrial, medical, and other applications that require highly complex and custom geometries for low to medium sized production runs. Learn more in our Materials for Metal 3D Printing guide.
Plastics
Plastics are the most common material used in 3D printing, and offer a huge variety of choices for designers. PLA, PC, ABS, PC-ABS, and PP are some of the most common plastics, but others are also readily printable such as HDPE, LDPE, PEEK, PTFE, and other high performance plastics. In SLA type printers, thermoplastic resin is also a popular choice for its surface finishes, optical qualities, and enhanced rigidity over other plastics. Large scale 3D printers using plastic can achieve a print volume up to 3’ x 2’ x 3’, however with parts bonding the sky's the limit to the maximum achievable size. The applications for plastics in 3D printing are essentially endless, but some of the most common ones include rapid prototyping, spare parts production, disposable applications, decorative and aesthetic applications, and basic components.
Specialty Materials
With the continuous development of new 3D printing materials, there has been a number of advancements that can be implemented using specific systems such as carbon fiber, nitinol, ceramic composite, graphene/graphite, impregnated, and other specialty materials in additive manufacturing. Speak with our manufacturing experts if interested in using a specific nonmetal/nonplastic material, and they can provide the maximum part size and parts bonding options. Specialty materials are still in development but find uses in scientific, general use, and industrial applications.
Looking for Large 3D Printed Parts?
Advantages of Large Scale 3D Printing
- Speed
- Single Part Production
- Cost and Labor Reduction

Speed
Large parts typically require long lead times to produce as they are either fabricated from large stock or are composites of bonded parts–with large format printing, these lead times significantly decrease and full parts can be made within a week or less. In agile or time-sensitive environments, the added manufacturing speed of large scale 3D printing frees up manufacturers for other aspects of the project while speeding up production without sacrificing quality.
Single Part Production
Parts printed in large 3D printers allow for parts consolidation and lessens the need for part bonding, allowing designers to not only save on manufacturing costs but decrease part count at the same time. Single part production is especially advantageous for applications that maximize strength and performance, as weld lines and other bonds are points of stress concentration and can hinder the overall efficacy of the part. Such advantages are needed in aerospace, defense, automotive, and other high-stress applications that rely on part integrity to effectively function.
Cost and Labor Reduction
3D printing is a much cheaper alternative to other additive manufacturing technologies such as injection molding or die casting, where a huge amount of investment goes into tool, core, mold, and pattern production. While the machine itself is expensive, large format printers provide both consistency and flexibility which is not found in other processes. Large scale 3D printing further reduces costs by decreasing the amount of bonding and post-processing needed on finished parts. 3D printing is also a relatively passive process once the design is loaded up and the print begins, eliminating the need for highly trained technicians and fabricators and instead only requiring a 3D printing technician familiar with the specific machine in use. Large companies looking to reduce overhead costs and optimize production runs can create huge savings with large format 3D printing systems.
Alternatives to Large Format 3D Printing
If large scale 3D printing does not fit your project, Xometry offers a variety of other services that can suit your requirements.
- Injection Molding
- Casting
- Thermoforming/Vacuum forming
Injection Molding
Injection molding is a thoroughly tested process used throughout many industries to additively produce large numbers of plastic parts. Injection molding uses high pressure to force liquified molten plastic into an injection mold, producing a part with excellent surface finish and consistency across thousands of mold cycles. Injection molding is best suited for plastic applications maximizing speed, efficiency, and cost reduction. To learn more, visit our page on Xometry’s Injection Molding Capabilities.
Casting
Casting is a process by which molten material (typically metal or plastic) is poured into a mold and is either placed under high pressure or is left to solidify, conforming to the mold’s shape. Casting is a centuries-old process that has had many advancements to its formula and is currently used throughout automotive, construction, consumer, medical, and many more industries thanks to its variety of available materials, versatility, and is an overall tried and tested additive technology. To learn more, visit our page on Xometry’s Die Casting Capabilities.
Thermoforming/Vacuum forming
Thermoforming or vacuum forming is the process by which a sheet of plastic is heated and then pressed between a mold and a core to produce a final part. Though limited to thin, uniform wall thickness parts, thermoforming is by far the easiest and cheapest manufacturing process when compared to other plastic forming applications, and can provide immense benefit if a part has a uniform wall thickness, is relatively simplistic, or is disposable.
Why Choose Xometry for Large Scale 3D Printing?
Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Easy to Use
Get your parts delivered right to your door without the hassle of sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.
Quality Assurance
We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, IATF 16949:2016, and AS9100D certified.