Custom Online Automotive Die Casting Service by Xometry
High Quality Die Cast Automotive Parts.
Automotive die casting is the process of injecting molten metal with a low melting temperature, such as zinc, aluminum, or magnesium, into a mold to create parts for the automotive industry. Die casting for the automotive industry has several advantages. It is an efficient way to manufacture lightweight parts, can be automated to greatly enhance manufacturing productivity, and is a highly flexible process that can be used to manufacture parts of all sizes.
Xometry offers the highest quality automotive die casting services: from the fabrication of major engine components and gearbox housings to wheels and suspension components. Choosing Xometry for automotive die casting ensures precise and high-quality components, quick turnaround, and exceptional customer service.
What Is Automotive Die Casting?
Automotive die casting is the process of pouring or injecting molten metal into a mold cavity to fabricate automotive components. The mold is held together by a hydraulic press that ensures the mold faces are precisely sealed. The molten material in the mold cavity cools and solidifies to form parts such as gearbox housings or engine blocks. Automotive die casting is a reliable, quick, and cost-effective way to manufacture large volumes of parts. It is a great alternative to other metal fabrication methods such as CNC machining or forming.
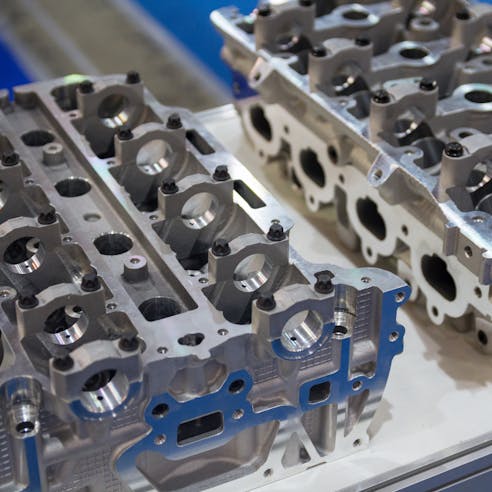

Types of Automotive Die Casting
The types of automotive die casting are hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting. Both types of die casting are commonly used in the automotive industry, but their use depends on the type of metal being cast and the application of the fabricated part. The two types are described in more detail below:
- Hot Chamber Die Casting
- Cold Chamber Die Casting
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Hot chamber die casting, also known as hot casting or gooseneck casting, is the more commonly used type of die casting. It is used for metals with low melting temperatures such as zinc, lead, and tin. Hot chamber casting is also known as gooseneck casting due to the shape of the feed system that delivers the molten metal into the mold cavity. The feed system is submerged in a bath of molten metal within a furnace that melts the metal. A hydraulic piston is used to force the molten metal from the bath, through the feed system, into the cavity.
Hot chamber die casting can be used for the rapid production of large volumes of parts. However, since die-cast machine components are immersed in molten metal, corrosion is likely and routine maintenance is required to ensure reliable production.
Cold Chamber Die Casting
Cold chamber die casting, also known as cold casting, is used for metals with higher melting temperatures such as aluminum, magnesium, and copper, and for lower-volume production. In cold casting, metal is melted in a separate furnace and poured into a non-heated chamber where it is then injected into the cavity by a hydraulic piston.
Cold chamber die casting is the lower cost option between the two types of die casting since it requires less maintenance. However, the process can lead to more variability in product quality due to temperature variations throughout the process. Additionally, cold chamber die casting is a slower process than hot casting since the injection temperature must stabilize to ensure consistent, good-quality parts.
Advantages of Automotive Die Casting
There are several advantages of automotive die casting compared to other traditional metal fabrication methods. These advantages are listed and described below:
- Fabrication of Lightweight Components
- Enhanced Automation and Flexibility
- Increased Productivity
- Precise, Complex Parts
- Increased Sustainability of Components

Fabrication of Lightweight Components
Automotive die casting is an efficient and effective way to fabricate lightweight components. Zinc, aluminum, copper, and magnesium are all much lighter than heavier metals such as steel. Lightweight components allow manufacturers to save money on transportation and delivery costs, which consequently leads to lower prices for consumers. Additionally, lightweight parts enable more energy-efficient vehicles, which reduces carbon footprint. So consumers, manufacturers, and the world at large stand to benefit from lighter automobiles.
Enhanced Automation and Flexibility
Compared to other methods like CNC machining, automotive die casting is a fast and reliable method of manufacturing large quantities of parts for vehicle production. Automotive die casting is a highly automated process that can be used to create both large and small parts for several different automotive applications. OEMs and aftermarket suppliers utilize die casting to produce parts such as wheels, vehicle chassis, paneling, and suspension components. These parts can be rapidly produced and used on different vehicles to be sold as OEM replacements, spare parts, or aftermarket parts.
Increased Productivity
Automotive die casting enhances manufacturing productivity since labor input per fabricated unit is much less than for other manufacturing processes such as CNC machining or forming. Parts with complex and intricate designs, such as engine blocks and wheels, can be quickly made in a single operation as opposed to CNC machining which may require several tool changes and workpiece adjustments before parts are completed. The enhanced productivity enables manufacturers to reduce unit costs which can then translate to increased profit.
Precise, Complex Parts
Automotive die casting fabricates complex parts with high dimensional accuracy and durability. The metals commonly used for die casting have low thermal expansion coefficients which ensure dimensional accuracy in harsh conditions and over time.
Increased Sustainability of Components
Automotive die casting leads to increased sustainability of components due to the fabrication of eco-friendly and sustainable components. The metals commonly used in automotive die casting, zinc, aluminum, and magnesium, are easily recyclable.
Disadvantages of Automotive Die Casting
Automotive die casting is not without its disadvantages. The disadvantages of automotive die casting are listed below:
- Increased Costs
- Prone to Defects
- Support Non-Ferrous Metals Only

Increased Costs
Both the molds and the machinery required for automotive die casting can be expensive. Additionally, maintaining molds and equipment over time leads to even more costs. Due to the large capital investment required upfront and throughout its life, automotive die casting is typically only ideal for large production volumes.
Prone to Defects
Die casting is a closed system and does not allow any substances to enter or exit the mold cavities prior to the part fully solidifying and ejecting. Because molten metal rapidly fills the cavity and there is no way for air to escape, gas bubbles can form in casted parts. These bubbles can adversely affect the strength and integrity of parts. Additionally, other defects such as misruns or cold shuts can occur.
Support Non-Ferrous Metals Only
Die casting only supports non-ferrous metals and cannot be used to process metals such as iron and steel. The high melting points and susceptibility to oxidation and corrosion can significantly reduce mold and die casting machine life. Additionally, the complexity of ferrous metals and the behavior of their grain structures at different temperatures make die casting undesirable.
Automotive Die Casting Metals
Xometry offers several different metals for automotive die casting including: zinc, aluminum, and magnesium. These materials and their use in die castings are explained in more detail below:
- Zinc
- Aluminum
- Magnesium
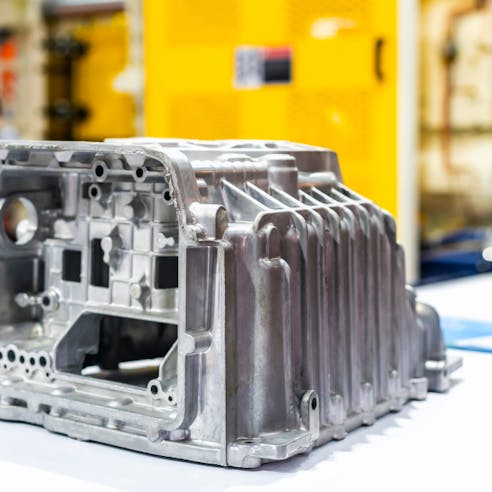
Zinc
Zinc is commonly used in hot chamber die casting and makes up approximately 28% of all automotive die-cast parts. Its high strength and ductility, corrosion resistance, dimensional stability, and thermal and electrical conductivity properties make the metal highly desirable for a number of applications. Such applications include chassis parts, retractor gears, seat-belt pulleys, and door-lock housings.
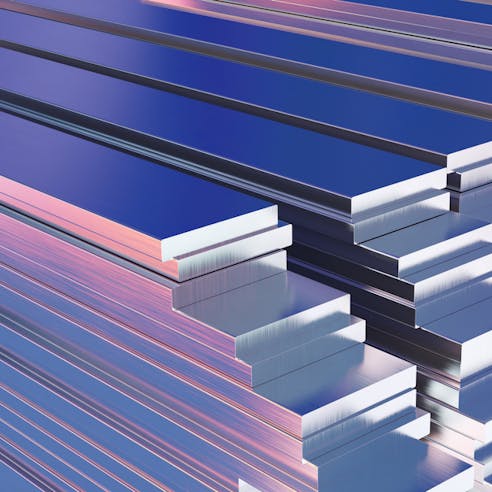
Aluminum
Aluminum is typically used in cold chamber die casting and is valued for its lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, recyclability, and dimensional stability. A380, 383, and B390 are the most common aluminum alloys used in automotive die casting. Aluminum is often used to cast components such as gearbox cases, engine brackets, cylinders, and chassis components.
Magnesium
Magnesium is commonly used in cold chamber die casting and is ideal for automotive die casting due to its light weight, strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and environmental friendliness. Magnesium is often used to cast components in power trains, seat frames, instrument-panel housings, and more.
Applications of Die Casting in the Automotive Industry
Several parts in the automotive industry are produced by die casting. Some examples of automotive die-cast parts are listed below:
- Engine Parts
- Mounting Brackets for Motors
- Protective Enclosures for Critical Equipment
- Shielding for Electronics and Telematics
- Housings for Airbag Sensors
- And more!
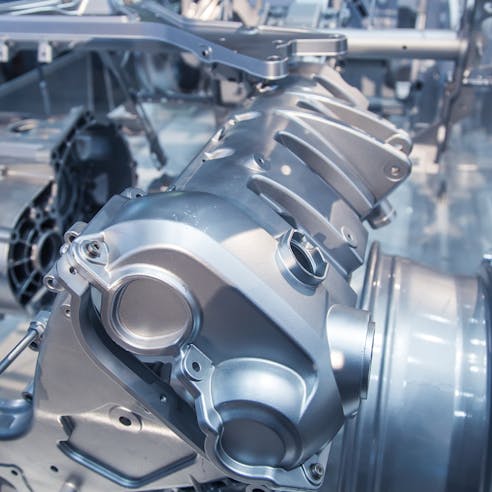
- Engine Parts: Parts like cylinder heads and gas engine parts are typically made from aluminum and magnesium through cold chamber die casting.
- Mounting Brackets for Motors: Large volumes of mounting brackets for electric motors and stepper motors can be made quickly through die casting. These parts are typically made from zinc, magnesium, and aluminum through both hot and cold die casting.
- Protective Enclosures for Critical Equipment: Covers for gearboxes, electronics, motors, and more are often made from zinc through hot die casting.
- Shielding for Electronics and Telematics: These components are often fabricated from zinc through hot chamber die casting.
- Housings for Airbag Sensors: Housings for interior components are often made from zinc through hot chamber die casting.
- Fuel Intake Components: Both aluminum and magnesium are often used to fabricate fuel-intake components through cold die casting. This is because both materials are thermally stable.
- Air-Conditioning Components: Air-conditioning components are often made from zinc through hot die casting.
- Seat-Belt Retractor Spools: These components are commonly zinc die-cast parts. Zinc’s durability and hardness make it an ideal metal for this application. Hot chamber die casting is commonly used to make these parts.
- Intricate Lock Barrels: Components for door locks are commonly made from zinc due to the metal’s strength, durability, and hardness. Hot die casting is commonly used.
- Transmission and Chassis Components: Both aluminum and zinc are commonly used for transmission and chassis components due to their high strength and corrosion resistance. Both hot and cold casting is used to make these parts.
- Connectors for Autonomous Vehicles: Connectors are often made from aluminum due to their excellent electrical conductivity. Cold die casting is typically used to fabricate connectors.
- Lidar Housings: Lidar housings are often made from zinc or aluminum through hot or cold die casting.
- Brake and Power-Steering Components: These components are often made from zinc due to their durability, hardness, and strength.
Alternatives to Automotive Die Casting
Some components cannot be fabricated by die casting due to geometry that makes parts non-moldable or because the intended metal is not suitable for die casting. Alternatives to automotive die casting are listed and described below.
- CNC Machining
- Forming
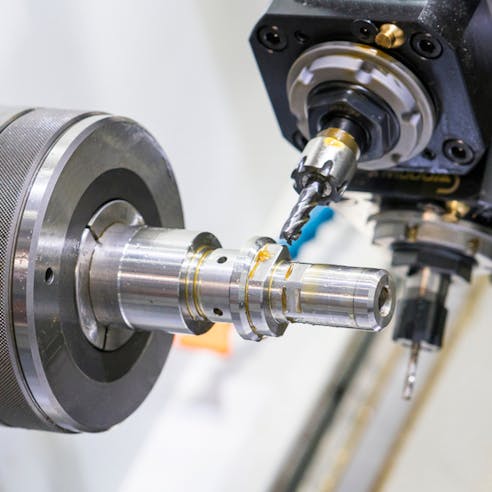
- CNC Machining: CNC machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that involves applying several different material removal processes (cutting, drilling, grinding, reaming, etc.) to a workpiece to obtain desired shape and size. While CNC machining is an effective way to produce large volumes of precise parts and fabricate parts from metals not suitable for die casting, die casting is a more efficient process. Die casting molds can have several cavities. Additionally, there are fewer processes to obtain a completed part with die casting than there are with CNC machining.
- Forming: Forming is a process that involves shaping metals into desired shapes using methods like stamping, extrusion, rolling, and forging. Forming processes are not as efficient as die casting but can be used to produce precise automotive parts.
Why Choose Xometry for Automotive Die Casting?

Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Easy to Use
Get your parts delivered right to your door without the hassle of sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.

Quality Assurance
We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, IATF 16949:2016, and AS9100D certified.