ABS Injection Molding Service on Xometry
Get custom ABS molded prototypes and production parts in as few as 10 business days. We provide expert engineering reviews and $500 off your first mold. Dozens of materials and finishes are available.
Xometry offers high-quality acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) plastic injection molding services for a variety of industries. Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene is a thermoplastic polymer that is easily worked, durable, and highly aesthetic. The ABS plastic injection molding process injects molten ABS under high temperature, and injection pressure into an injection mold, where the injected molded ABS parts are released and ready for use once cooled. Xometry’s ABS injection molding services are highly popular, as the high-volume plastic injection molding process combined with the low cost and material characteristics of ABS is ideal for industrial applications.
ABS Injection Molding Design Guidelines
Here are the typical design guidelines for ABS plastic injection molding. Note that these are general guidelines for the ABS injection molding process that may not accurately represent specific ABS plastic blends. Our Manufacturing Supplier Network of over 10,000 global partners can work outside these guidelines if they don’t fit your project requirements.
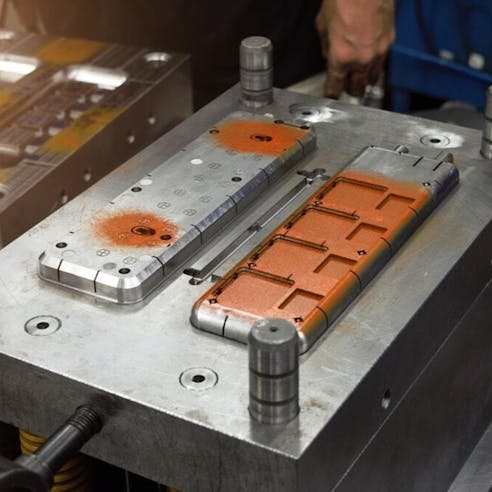
ABS Material Properties
Below is a table containing the material property ranges across various ABS plastics and ABS resins (general ABS, high impact ABS, low viscosity ABS, plate-able ABS, and other unique blends). Note that each ABS formulation will have a unique set of material properties depending on their intended application, and the table below provides a wide range of material characteristics.

| ABS Plastic Properties | Value |
|---|---|
ABS Plastic Properties Tensile Strength (Yield) | Value 13.0 - 65.0 MPa (1890 - 9430 psi) |
ABS Plastic Properties Flexural Modulus | Value 0.200 - 5.50 GPa (29.0 - 798 ksi) |
ABS Plastic Properties Impact Resistance (Izod Impact, Notched) | Value 0.380 - 10.3 J/cm (0.712 - 19.3 ft-lb/in) |
ABS Plastic Properties Maximum Service Temperature | Value 80.0 - 100 °C (176 - 212 °F) |
ABS Plastic Properties Chemical Formula | Value (C8H8·C4H6·C3H3N)n |
ABS Plastic Properties Chemical Resistance | Value Resistant to aqueous acids, alkalis, concentrated hydrochloric and phosphoric acids and animal, vegetable and mineral oils, but but weak to carbon tetrachloride, aromatic hydrocarbons, and concentrated sulfuric and nitric acids |
ABS Plastic Properties Glass Transition Temperature | Value 108 - 109 °C (226 - 228 °F) |
ABS Plastic Properties Heat Deflection Temperature | Value 88-89°C |
ABS Plastic Properties Melting Temperature | Value 170 - 320 °C (338 - 608 °F) |
ABS Plastic Properties Injection Molding Speed | Value 240 mm/sec (9.45 in/sec) |
Table values were obtained from data listed matweb.com
Advantages of ABS Injection Molding
The advantages of the ABS injection molding process include impressive dimensional stability and stability under load, its ability to be alloyed by other polymers, recyclability, and its aesthetic properties. For more information, see below:
- Good Dimensional Stability
- High Stability Under Load
- Easily Alloyed with Other Polymers
- Recyclable
- Aesthetically Pleasing

Good Dimensional Stability
ABS plastic is dimensionally stable at ambient temperatures up to its maximum service temperature. This advantage makes ABS valued as a cost-efficient material for applications where other plastics would bend or warp under similar conditions, such as fittings, vacuum system components, or housings.
High Stability Under Load
ABS plastic will retain its stability and rigidity under load up until its heat deflection temperature, making it useful for load-bearing applications such as brackets, fasteners, snap fits, and other load-carrying applications.
Easily Alloyed with Other Polymers
ABS plastic easily incorporates into other polymers to form alloys, where ABS’s rigidity, scratch resistance, and dimensional stability are paired with another polymer’s attributes to make a material better than its sum. This ability has allowed the formulation of another highly popular polymer blend, PC-ABS, which retains ABS’s strength but is also more resistant to heat and impacts. This makes ABS an attractive choice for polymer manufacturers when making application-specific plastic grades.
Recyclable
Once the life of an ABS plastic part is complete, it can be fully recycled back into ABS material by grinding the part and re-melting it into stock material alongside new ABS. The recycled ABS cannot be melted down into new stock by itself and requires fresh ABS to retain its properties, as successive heat cycles from ABS plastic molding degrade its chemical structure. The recyclability of ABS allows it to function in roles where sustainability and cost reduction are important. Note that ABS is recyclable but not biodegradable, as it is a petroleum-based thermoplastic.
Aesthetically Pleasing
ABS plastic can achieve a variety of colors and a high gloss finish with the use of acetone vapor or other finishing processes. ABS plastic is, therefore, an ideal plastic for toys, models, and other applications where looks are of key importance.
Ready to Get a Custom ABS Injection Molding Quote?
Disadvantages of ABS Injection Molding
The disadvantages of ABS plastic injection molding include poor temperature control, poor chemical resistance to certain substances and environments, poor friction and wear resistance, and a tendency to off-gas toxic fumes when heated. For more information, see below:
- Poor Temperature Control
- Poor Solvent and Fatigue Resistance
- Substandard UV Resistance Unless Protected
- Poor Friction and Wearing Behavior
- Toxic Fumes/ Highx` Smoke Evolution

Poor Temperature Control
Though resistant to temperatures up to 100 °C, ABS plastic generally does not like heat and has a range of temperatures where it is not easily controllable. This makes ABS injection molded parts non-ideal for heat exchangers or other components that will regularly experience cycles of heat above its service and heat deflection temperatures.
Poor Solvent and Fatigue Resistance
ABS experiences severe effects with acetone, carbon tetrachloride, aromatic hydrocarbons (including fuel oils), and concentrated sulfuric and nitric acids. In the presence of these substances, ABS plastic will swell or may dissolve completely, making it unsuitable for chemical containers or handling equipment that may be in contact with a variety of organic and inorganic chemicals, such as injection molded parts for chemistry labs.
Substandard UV Resistance Unless Protected
ABS plastic will degrade in the presence of ultraviolet (UV) light, such as those radiating from the sun–that is, unless it is formulated with UV resistance in mind where it is alloyed with another polymer or otherwise treated with UV resistant strengtheners. ABS is, therefore, not a good material for outdoor equipment by itself, requiring these additives to function.
Poor Friction and Wearing Behavior
ABS is generally not specified for its friction or wear resistances, especially when considering its tendency to weaken when heated. Some blends attempt to remediate this weakness with additives like carbon fiber. However, pure ABS is not suitable for injection molded parts for bearings, friction components, or otherwise high-wear environments.
Toxic Fumes/ High Smoke Evolution
When heated far above its melting temperature, ABS will release toxic fumes, which are both pollutants and a health concern to those who inhale them. This concern is pertinent to injection molding applications where potentially hundreds of kilos of ABS a day are heated and where tight temperature controls must be used to prevent smoke evolution and toxic off-gassing.
ABS Injection Molding Applications
ABS plastic molding is widely used throughout industry as a general-purpose engineering material, thanks to its exceptional blend of abundance and material properties. Here are some of the most common applications of ABS injection molding in industry.
- Automotive
- Electronics
- Appliances
- Fittings
- Recreational Products

Automotive
Automotive applications leverage ABS plastic molding to fabricate parts from interior components to switches even to engine components like clasps and fasteners. In larger injection molding machines, ABS can even be used to make door or body components. The economic efficiency per part of both injection molding and ABS make it ideal for high-volume applications like vehicle manufacturing.
Electronics
ABS plastic molding is ideal for building electronic housings and non-conductive components. Not only is it insulative, but it can be injection molded into highly complex shapes and in a variety of aesthetic colors and finishes. ABS injection molding also reduces the overhead costs for the high-volume manufacturing of personal electronics.
Appliances
Appliances like kitchenware, vacuum cleaners, washing machines, and other household tools benefit from the aesthetic-yet strong profile of ABS injection molded parts. Just as with other applications, this process can help decrease the price of these tools while also providing more profit to suppliers.
Fittings
General fittings and fasteners made from ABS plastic molding are inexpensive, plentiful, and can be designed with complexity in mind.
Recreational Products
Recreational goods such as sports equipment, toys, models, furniture components, and other products all benefit from the cost-effectiveness of ABS injection molding, offering a variety of complex shapes for consumers that are well within their budgets.
Alternatives to ABS Injection Molding
If Injection molded ABS does not seem like a good fit for your project, Xometry has an extensive portfolio of alternate plastic molding services and manufacturing tools to help you bring your ideas to life.
- ABS FDM 3D Printing
- ABS CNC Machining
- Large Part Injection Molding
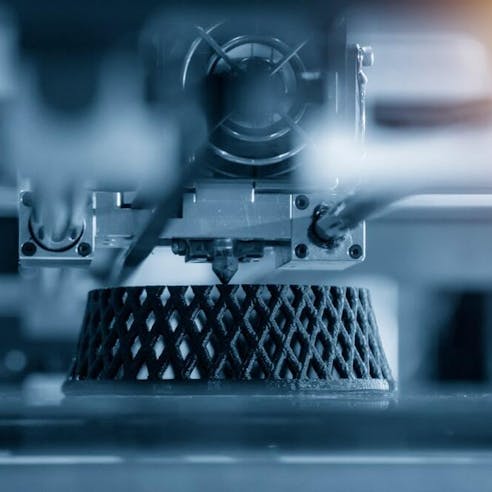
ABS FDM 3D Printing
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing offers a high-volume, low-cost alternative to injection molding. ABS FDM 3D prints can achieve comparable design complexity to ABS injection molding and also offers a wide range of thermoplastic blends to choose from. To learn more, view our capability page on our ABS FDM 3D Printing Service.
ABS CNC Machining
If your projects require subtractive manufacturing processes, Xometry provides highly accurate and expedient ABS CNC machining for your parts. To learn more, view our capability page on our ABS CNC Machining Service.
Large Part Injection Molding
If the size of parts is of primary concern and not necessarily the material, then large part injection molding offers a variety of materials for the biggest of ideas. Designers can choose from general-use plastics to engineering materials that can be made in sizes much larger than the typical injection molding machine. To learn more, view our capability page on our Large Part Injection Molding Service.
Why Choose Xometry for ABS Injection Molding?

Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Easy to Use
Get your parts delivered right to your door without the hassle of sourcing, project management, logistics, or shipping.

Vetted Network
We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, and AS9100D certified. Only the top shops that apply to become Suppliers make it through our qualification process.