Micro Molding Services
Xometry offers the highest quality micro molding services and can assist in the production of parts with intricate and complex geometries and excellent surface finishes. Subject to availability. Xometry doesn't guarantee that we can provide this service at any given time.
Micro molding is a highly advanced and specialized manufacturing process that enables the fabrication of complex, miniature parts with incredible precision. Considered a subset of plastic injection molding, micro molding is tailored for producing parts with features typically less than one millimeter. It has gained prominence in industries like: medical device manufacturing, electronics, automotive, and aerospace. The ability to efficiently create precise parts with minute features in large volumes and in a wide range of compatible materials are some of the biggest advantages of custom plastic injection micro molding.
Xometry offers high-quality micro molding services for a variety of industries and applications. Common applications for micro injection molding include integrated circuit components and automotive door-locking mechanisms. Our vast manufacturing network coupled with our extensive manufacturing experience ensures your parts will be made to the highest standards of quality with short lead times.
The Micro Injection Molding Process
The micro molding process is nearly identical to the standard plastic injection molding process but requires more careful control to ensure high-quality parts. Before micro injection molding can actually begin, molds and die sets must be fabricated. Precise and advanced manufacturing methods such as electric discharge machining (EDM), micro EDM, and micro-machining are used to create extremely precise molds with tolerances as small as a few micrometers. Once fabricated, molds can be mounted in a micro injection machine. Then, a thermoplastic or liquid silicone rubber is melted and maintained at a consistent temperature. The molten material is forced into the micro mold with a controlled flow rate and held at a particular pressure while it cools. Advanced programming and controls within micro injection molding machines ensure molding parameters are stable and consistent. Once sufficiently cooled, the micro injection molded parts are ejected from the mold and inspected to ensure dimensional tolerances are met.
Types of Micro Molding Processes
There are various types of micro molding, each with its own sets of advantages and disadvantages and special use cases. The different types of micro molding processes are listed and described below:
- Insert Molding
- Overmolding

Insert Molding
Insert molding is a type of injection molding in which a metal component is placed into a mold cavity before molten plastic fills the mold. Insert molding is also possible with micro molding. In the insert micro molding process, a metal insert is positioned either manually or automatically by a robotic arm in the mold. Then, the mold closes, the plastic resin is injected in a single shot, and the molten plastic forms around the insert to create a single part. Finally, the part is ejected, the metal insert is removed, and the process repeats. Insert micro molding is a great way to enhance product durability and functionality. It is commonly used in the medical manufacturing industry to make components like catheters or in the electronics industry for micro-optic and integrated circuit components.
Overmolding
Overmolding is another subset of injection molding. It is the process of molding different materials or different colors of the same material in the same mold to create complex multi-material or multi-color parts. As with typical injection molding, the overmolding process begins with the injection of a substrate material into a mold. Then, a second injection is made using a different material or the same material with a different color into the same mold. The material from the second injection is layered directly on top of the first layer. This results in a single solid piece composed of different materials or colors. The process is great for enhancing grip characteristics for consumer products and attractive, multi-color products. Micro overmolding is often used to create small parts like: multi-color buttons or housings for electronics and seals and gaskets in automotive.
Material Selection for Micro Molding
Material selection is highly important in micro molding projects as thermoplastic polymers and other specialized resins must be carefully vetted for suitability for particular applications, particularly in medical applications. The different materials used in micro molding are listed and described below:
- Polyethylene (PE)
- Polypropylene (PP)
- Nylon (Polyamide)
- Polycarbonate (PC)
- Delrin® (Acetal / Polyoxymethylene / POM)
- Polysulfone (PSU)
- Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
- Acrylic (Polymethylmethacrylate / PMMA)
- PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
- ULTEM® (Polyetherimide / PEI)
- LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer)

Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene is one of the most commonly used thermoplastics in the world. Polyethylene is an FDA-compliant material, which makes it suitable for food and beverage applications. Additionally, it has great chemical and thermal resistance, as well as high tensile strength. Common applications of PE include: packaging, consumer goods, and textiles.
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is another popular plastic used for components in a variety of industries and applications. Desirable properties of PP include: rigidity, wide operating temperature range, and chemical, corrosion, and fatigue resistance. Common applications of PP include: packaging, machinery components, textiles, and consumer goods.
Nylon (Polyamide)
Nylon is a popular thermoplastic lauded for its chemical resistance, strength, and dimensional stability across a wide temperature range. Nylon has many uses including: textiles, electrical housings, and mechanical components like bearings, bushings, and sprockets.
Polycarbonate (PC)
Polycarbonate is a thermoplastic known for its transparency, optical clarity, tensile and impact strength, recyclability, and chemical and fire resistance. These properties make polycarbonate great for electrical housings, switches, machine guards, and more.
Delrin® (Acetal / Polyoxymethylene / POM)
Delrin® is DuPont’s trademarked polyoxymethylene (POM or acetal) resin. Delrin® is known for its strength, toughness, elasticity, rigidity, chemical and flame resistance, machinability, dimensional stability, and low friction coefficient. POM is used for mechanical components such as: gears, pulleys, and rollers.
Polysulfone (PSU)
PSU is a translucent thermoplastic known for its biocompatibility, food compatibility, good mechanical properties, and wide operating temperature range. PSU is commonly used in food preparation and medical industries due to its bio-friendliness.
Polybutylene Terephthalate (PBT)
PBT is a thermoplastic that has great dimensional stability, high strength, good chemical, UV, and thermal resistance, and low moisture absorption characteristics. PBT is often used in the automotive and electronics industries for automotive fenders, electrical enclosures, and power-tool housings.
Acrylic (Polymethylmethacrylate / PMMA)
Acrylic is a widely used thermoplastic due to its optical clarity and transparency, high tensile and impact strength, light weight, and durability. PMMA is often used as a substitute for glass and is commonly used in applications like: signage, windows, machine guards, and more.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
PEEK is a special thermoplastic that is known for its wide operating temperature range up to 489 °F or 250 °C. Not only that, but it also has high strength, great chemical resistance, and high stiffness. PEEK is used in a variety of applications, from mechanical components like: bushings, bearings, and seals to fluidic components like valves and fittings, electrical housings, and connectors.
ULTEM® (Polyetherimide / PEI)
ULTEM® is a popular brand name for the thermoplastic PEI. PEI is known for its rigidity, high mechanical strength, and creep resistance over a broad range of temperatures. Additionally, PEI is a great electrical insulator, which makes it commonly used for applications like coils and fuses in electronics and interior trim pieces in aircraft.
LCP (Liquid Crystal Polymer)
LCPs are advanced polymer materials that maintain an ordered microstructure in both liquid and solid phases. The ordered microstructure results in exceptional mechanical strength and great temperature and flame resistance. Uses of LCP include: electrical connectors, catheters, surgical and dental instruments, and coatings on cookware.
Micro Molding Advantages
Micro molding offers many advantages for manufacturers and end users. These advantages are listed below:
- Lightweight
- Size
- Less Energy and Time
- Tight Tolerances
- Chemical Resistance

Lightweight
Micro molding creates parts that are lightweight and small. This is particularly useful for creating small and comfortable medical implants. Additionally, lightweight micro molded parts are also important in the creation of small, lightweight electronics or microfluidic components like small valves and fittings.
Size
Not only are the parts made by micro molding lightweight, but they are also exceptionally small in size. Advanced machining processes like micro-machining and EDM are used to create small, precise mold cavities and cores. As a result, micro-molded parts can easily fit into small and confined spaces. Micro molding has become a popular process for creating small parts in electronics, medical implants for orthopedics, pacemakers, and micro-optics.
Less Energy and Time
Micro molding offers significant cost savings compared to conventional injection molding. The cost savings are a result of the smaller tools and machinery needed to complete the micro molding process. Tools and molds are often smaller in size and thus cheaper to manufacture. Additionally, because parts are smaller, clamping forces are smaller, and consequently, power requirements are smaller. Finally, since parts are smaller, cycle times are often shorter since parts do not require as long a time to cool compared to parts made from conventional injection molding. All these traits of micro molding enable significant cost savings.
Tight Tolerances
Creating parts that satisfy tight tolerances is something the micro molding injection molding technique excels at. Micro molding enables the production of exceptionally small, detailed, and complex components with tolerances as small as 0.005” to 0.015”. Advanced manufacturing methods like micro-machining and EDM allow micro-sized cavities, cores, and other features to be made with great accuracy. The process is often used in the fabrication of electronics, medical devices, and micro-optics because of its ability to produce parts that satisfy tight tolerances.
Chemical Resistance
Thermoplastics used in the micro molding process often exhibit great chemical resistance. Therefore, the miniature parts created by the process can be used in applications with high exposure to various chemicals or in corrosive environments. This is particularly useful in the medical industry for implants, instruments, and diagnostic equipment, as well as in fluidic control components like valves and fittings. Additionally, various consumer goods and electronics may benefit from the chemical resistance offered by micro molded parts.
In need of custom micro molding services?
Micro Molding Applications
There are many different industrial applications of micro molding, some of which are listed and described below:
- Medical Devices
- Drones
- Surveillance Equipment
- Fitness Trackers
- Robotics
- Automotive Industries

Medical Devices
Medical devices require parts to be made to stringent dimensional standards to ensure healthy patient outcomes and safety. Medical devices are one of the biggest applications of micro molded parts. The different applications in which micro molding is used in medical devices are listed below:
- Implants
- Catheters
- Drug delivery systems
- Diagnostic equipment
Common materials for micro molded parts in the medical industry include: PE, PP, and PC.
Drones
Drones are uncrewed, remotely controlled, or programmed aircraft that are used for many applications—from surveillance to hobbyist uses. Lightweight micro molded components are important for the function and performance of drones. Micro molded components in drones include:
- Housings, switches, and connectors for optical equipment
- Actuators and gears
- Sensor housings
- Structural components
PC, acetal, acrylic, PEI, nylon, and more are used for micro molded drone components.
Surveillance Equipment
Surveillance equipment that utilizes optical devices such as CCTV cameras and body cameras is another application of micro molded components. As electronics become smaller, the components in electronics must satisfy tighter tolerances and more stringent precision requirements. Below are some examples of micro molded components for surveillance equipment.
- Lenses
- Mirrors
- Plugs
- Switches
Plastics like PE, PP, and acrylic are commonly used in micro molded parts for surveillance equipment.
Fitness Trackers
Fitness trackers are popular medical and consumer electronic devices that track important health information such as: heart rate, breathing rate, distance traveled, and time asleep. These devices must be small and minimally invasive to optimize user comfort while maintaining functionality. Micro molded parts for fitness trackers include:
- Switches
- Housings
- Plugs
Nylon, acrylic, and PC are common materials in fitness trackers.
Robotics
As with surveillance equipment and fitness trackers, the electronics used in robotics are small and must satisfy small dimensional tolerances. Micro molded parts help reduce the weight of robotics while also helping them improve performance and function. Different applications of micro molded products in robotics include:
- Sensor housings
- Switches and connectors
- Gears and actuators
Acetal, PP, PC, PE, and acrylic are commonly used for micro molded parts in robotics.
Automotive Industries
Micro molding enables automotive parts to be smaller. This results in lighter, more fuel-efficient, and better-performing vehicles. Applications of micro molding in the automotive industry include:
- Components in brake pads and assemblies
- Fastening hardware such as washers and clips
- Door locking mechanisms
- Switches
- Micro gears
- Buttons
Other Features of Xometry Micro Molding Services
Listed below are the other features of Xometry’s micro molding service:
- Surface Finish
- FDA Registered
- High-Volume Production
- Drug Delivery Devices
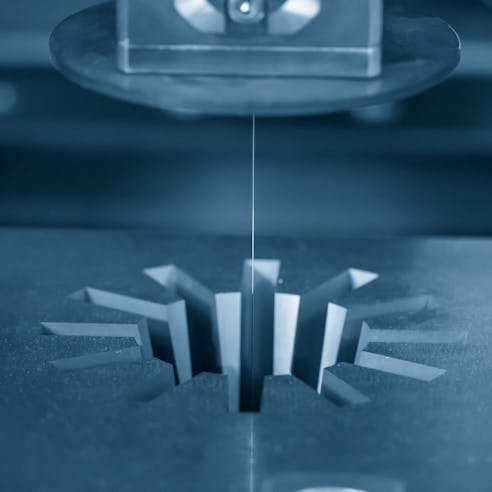
Surface Finish
Surface finish is a significant factor for micro molded parts, not only when it comes to aesthetic appeal, but also the functionality of a micro molded product. Advanced manufacturing methods like micro-machining and EDM are used to attain precise dimensions in the cavities of small micro molds. While EDM can be used to achieve precise dimensions, it also has the ability to create desirable mold textures in cavities that lead to smooth, finished parts.
FDA Registered
FDA standards regulate devices and components that can be used in the medical industry. Xometry is ISO 14385 certified and has extensive manufacturing and industry experience. This means your micro molded parts are fabricated to the highest standards of quality and to comply with regulatory standards.
High Volume Production
High volumes of precise parts can be made with micro molding just like with standard injection molding. Molds used in micro injection molding can have multiple cavities which enable the production of several parts in a typical 30 to 60 second cycle time. Manufacturers can easily produce hundreds to thousands of parts a day with micro molding.
Drug Delivery Devices
Drug delivery devices are medical devices that deliver and/or control the release of a medicine or therapeutic agent to specific sites in the human body. Typical drug delivery can be accomplished by digestion, inhalation, injection, or topical techniques. However, advancements in medicine have led to the use of micro molding to create drug-delivery devices with new methods for administering medicines. Microneedle patches that have an array of tiny needles thinner than a strand of hair and small robotic pills that help treat various digestive disorders are examples of drug delivery devices that utilize micro molding. Xometry’s micro molding capability enables the fabrication of such devices.
Alternatives to Micro Molding
Xometry offers alternative methods for micro molding as listed below:
- 3D Printing
- Micro-Machining
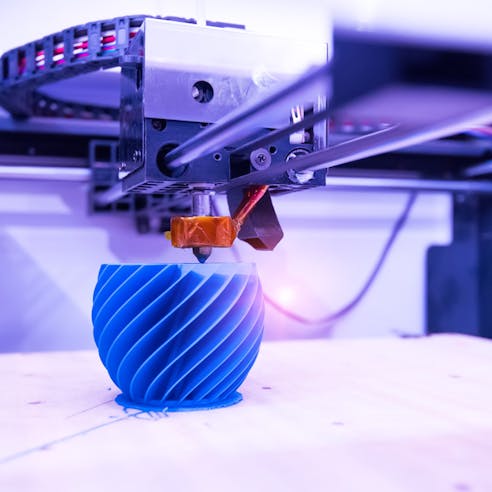
- 3D Printing: 3D printing is a great alternative to micro molding due to the process’s ability to produce tiny plastic or metal parts with complex features. 3D printing is the process of producing parts layer-by-layer until the complete 3-dimensional part is created. 3D printing methods such as stereolithography (SLA), digital light processing (DLP), selective laser sintering (SLS), and selective laser melting (SLM) can achieve precise dimensions as small as +0.010. While 3D printing can achieve tolerances similar to micro molding, the process is often more expensive due to the equipment required and the slower processing time.
- Micro-Machining: Micro-machining is a subset of CNC machining that encompasses micro CNC milling or micro-electric discharge machining (µEDM). Micro CNC milling can achieve tolerances as low as 0.001”, while µEDM can achieve tolerances as small as 0.008” or 0.02 mm. While micro-machining can achieve similar tolerances to micro molding, the process is often more expensive due to the cost of µEDM machines and the slower process involved.
Why Choose Xometry for Micro Molding Services?

Endless Options
Choose from millions of possible combinations of materials, finishes, tolerances, markings, and certifications for your order.

Easy to Use
Get started with our easy-to-use platform and let our experts take care of managing the project from locating the right manufacturing partner to delivery logistics.

Vetted Network
We are ISO 9001:2015, ISO 13485, and AS9100D certified. Only the top shops that apply to become Suppliers make it through our qualification process.