It’s no small feat to get a plane into the air, and before a pilot can even maneuver it through the sky, it needs all the right parts, components, and functioning systems in place. Building an aircraft is complex, but as technology advances, many processes are simplified, automated, and improved, and one futuristic-sounding operation, in particular, is lightening the load for engineers and manufacturers: 3D printing.
There are many ways in which additive manufacturing is making the future brighter for the world of aircraft creation, but we’ve broken down some of the most impressive and impactful ways in the article below and included services and resources Xometry has available for manufacturing aerospace and defense parts for your own company.
1. Simplify the Parts
Plane parts are typically complex and involve multiple components coming together without fault, which can be a tricky thing to achieve. With 3D printing, these parts can be turned into one streamlined design that’s materialized by a 3D printer. That means the process of getting flight parts is easier and there’s a lower risk of failure. If you’re in this sector, you can get instant and confidential quotes for flight parts through Xometry, too.
2. Fast Production
Rather than waiting on a specific manufacturer to fix or deliver a part or suffer through long wait times, 3D printing makes it easy to print components on demand and do so all in one place. This drastically cuts down on lead times, makes it far easier to take care of urgent repairs and maintenance problems, and simplifies the prototyping process.
3. Weight Reduction
Passengers, pilots, and manufacturers are all very familiar with the importance weight has on an aircraft’s performance and fuel efficiency. While cargo and luggage are a part of that, one of the most crucial ways that weight can be cut down is through building lighter components — something 3D printing utterly excels at. With a printer, you can construct flight parts made of plastic polymers, lighter metals, or other lightweight materials that are better optimized and not nearly as heavy as traditional structures, doors, or engines.

4. Improved Aircraft Design
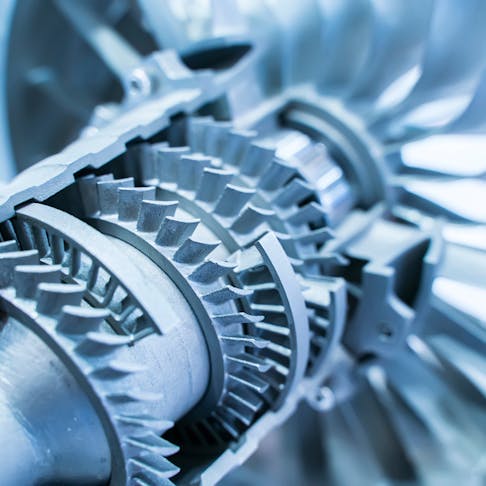
With more traditional manufacturing methods, it’s not always possible to create innovative and novel designs or test out inventive new ideas, but with 3D printing, the world of engineering has completely expanded. Not only can we create parts that are more aerodynamic and better functioning, but there’s room to trial unique new designs such as sleek turbines or stylized cabin interiors. As you can see in the image below, this is an example of what a 3D-printed airplane part looks like.
5. Improved Supply Chain
The metaphorical headache caused by long lead times and complex logistics can be nearly eliminated with the help of 3D printers. Companies will no longer have to lean on extra-long chains and the hold-ups caused by one supplier or manufacturer that cause a domino effect of problems. Printing happens on demand with additive manufacturing, so parts can be made in-house and whenever needed — meaning there’s no longer a reason to store parts in enormous inventory warehouses or wait around for something to be made. It also gives back some control to your own supply chain, which is always a bonus for the folks who run aircraft companies.
6. Reduced Supply Chain Cost
It’s no secret that the costs to build an aircraft are astronomical, especially custom parts and larger commercial planes. Fortunately, this is another area where 3D printing can make a positive impact by cutting down expenses. Parts of the overall cost include transportation, tooling, storage, and inventory management — most of which can be cut out or cut down through additive manufacturing. There is also a lot of money lost through obsolete parts, but with on-demand printing, this problem will be a rarity since designs can constantly change and parts won’t have to be physically stored.

A 3D Printed Aircraft Part
What was the Aircraft Manufacturing Industry Like Before 3D Printing Technology?
Before the advent of 3D printing technology, the aircraft manufacturing industry was stuck with so-called conventional manufacturing methods. The process went though time-consuming stages: design, prototyping, tooling, and assembly. Designers and engineers would create detailed blueprints and specifications for the aircraft components which would then be sent to specialized manufacturing facilities.
Conventionally speaking, repairs are time-consuming affairs. First, the specific part needs to be identified, which requires inspections and assessments. Then, the information is forwarded to the manufacturing facility responsible for producing the part. The manufacturing facility has to go through the lengthy process of creating the tooling required for production, which may mean designing and machining specialized molds or dies. Once the tooling is ready, the actual production can begin. This process takes considerable time due to the need for precision machining and assembly, quality control checks, and compliance with strict aviation regulations. Finally, the finished part is shipped to the aircraft maintenance facility, which adds further delays due to logistical considerations.
How Does 3D Printing Technology Evolve Over Time?
Additive manufacturing has already benefitted many industries, including the medical and automotive fields, and aviation is just one more branch it can support. Other ways you’ll see 3D printing impacting this world are through the development of cost-effective and fuel-efficient parts and by building with more eco-friendly materials. There is also much less wastage with this type of printing and consolidation of parts, so the sustainability aspect can really shine through.
3D printing can even improve the safety of parts, which is done by building with polymers and composites with better wear and heat resistance and longer-lasting durability. It’s also easier to make prototypes, so parts can be tested more often and more quickly than usual. Even more exciting is the fact that many of the industry's biggest players are already on board and using these technologies, including Airbus, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, GE Aviation, and Rolls-Royce, and they’re focusing extensively on using industrial-scale printers to build turbine blade, fuel nozzles, ducts, structural components, and cabin brackets.
What Role Does 3D Printing Play in the Design and Production of Aircraft Parts?
3D printing allows engineers and designers to create highly complex and optimized designs that would be difficult or impossible to manufacture using traditional methods. With 3D printing, intricate geometries, lightweight structures, and internal features are simple to build, leading to improved performance and efficiency of aircraft parts. 3D printing is also perfect for quick and cost-effective prototyping. Engineers can validate their designs, perform functional testing, and make design iterations in a shorter time frame.
How Does 3D Printing Improve the Performance and Safety of Aircraft Components?
3D printing enables engineers to optimize aircraft components for specific performance parameters. Components can be analyzed and refined to maximize strength, durability, and efficiency through advanced software tools and simulation techniques. 3D printing also enables the use of advanced materials with specific properties and performance characteristics. The specialized polymers, composites, and even metal alloys are themselves frequently optimized for strength, heat resistance, and durability. These materials can be tailored to meet the stringent requirements of aircraft components, ensuring safety and reliability in demanding operating conditions. Additionally, 3D printing allows for the rapid production of prototypes for iterative design and testing processes. Engineers can quickly produce functional prototypes and test them in real-world conditions to evaluate performance, identify potential issues, and make necessary design improvements.
What are the Environmental Benefits of Using 3D Printing in Aircraft Manufacturing?
The use of 3D printing in aircraft manufacturing offers several environmental benefits, including:
- Reduced Material Waste: Most 3D printers use only enough material to create a component. It doesn’t need to be machined off and discarded. This reduces material waste and conserves resources.
- Lightweight Design: 3D printing enables the creation of complex and lightweight designs that aren’t attainable with conventional manufacturing techniques. Less mass equates to lower fuel consumption and thus minimizes greenhouse emissions.
- Consolidation of Parts: Additive manufacturing lets you consolidate multiple components into a single part. Fewer separate parts also mean fewer fasteners and joints. This again minimizes weight, streamlines assembly, and ultimately improves the aircraft’s energy efficiency.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: 3D printing enables on-demand manufacturing, which reduces the need for large-scale production, warehousing, and transportation of pre-manufactured components. Manufacturers can produce parts as needed, reducing inventory requirements, waste, and associated carbon emissions from transportation and storage.
- Sustainable Materials: The evolution of 3D printing materials has included the development of eco-friendly and sustainable options. Most 3D printing materials are not biodegradable, but some newer ones are bio-based or derived from recycled sources, contributing to a more environmentally friendly manufacturing process.
- Extended Lifecycle and Repair: 3D printing can facilitate more efficient repairs and maintenance of aircraft components. Rather than replacing an entire component, specific sections can be 3D printed and integrated into the existing structure, extending the lifecycle of the component and reducing waste.
How Does 3D Printing Enhance the Speed and Efficiency of Aircraft Production?
3D printing enables rapid prototyping and iteration of designs. The ability to quickly produce functional prototypes allows engineers and designers to evaluate and test different design iterations in a much shorter time frame. This accelerates the product development process. 3D printing allows parts to be produced as they become needed, reducing inventory costs and the need for extensive storage. This on-demand manufacturing approach also minimizes supply chain delays; if you have access to your own printer, you can make components in-house and skip the sourcing delays entirely.
What New Opportunities Does 3D Printing Create for Aircraft Design and Innovation?
3D printing opens up new opportunities for aircraft design and innovation. A few are listed below:
- 3D printers can produce highly complex and intricate geometries that are challenging or impossible to manufacture using conventional methods.
- Multiple parts may be integrated into a single component, reducing the number of separate pieces and simplifying assembly processes.
- Personalized and one-off components no longer require individualized tooling. Each aircraft may have unique requirements or modifications.
- Designers can quickly produce functional prototypes for testing and evaluation, allowing for faster design iterations and refinement.
- Some advanced materials are easier to print than to manufacture by traditional methods. Lightweight alloys, high-strength composites, and other specialized materials often fit well into 3D printing processes.
- 3D printers can produce components on-site, reducing downtime and costs associated with maintenance operations and eliminating shipping delays.
How are Leading Aircraft Manufacturers Leveraging 3D Printing Technology?
Leading aircraft manufacturers actively use 3D printing technology to enhance their manufacturing processes, improve aircraft performance, and drive innovation. Some examples are listed below:
- Airbus uses additive manufacturing to produce components such as cabin brackets, wing brackets, and air ducts. Airbus has also partnered with Materialise, a 3D printing software and service provider, to develop software that optimizes the design and production of 3D-printed parts.
- Boeing has integrated 3D printing into their manufacturing processes, primarily focusing on prototyping and low-volume production parts. Many of their environmental control system ducts, structural parts, and tooling items are now printed. Boeing has also collaborated with Norsk Titanium to develop 3D-printed titanium structural components for their aircraft.
- GE Aviation makes extensive use of 3D printing in their aircraft engines. They have developed advanced fuel nozzles using additive manufacturing techniques, resulting in improved engine performance and fuel efficiency. GE Aviation has also invested in additive manufacturing research and development centers to further explore the potential of 3D printing in aerospace.
- Rolls-Royce 3D-prints components such as turbine blades and fuel nozzles. They have also partnered with the National Additive Manufacturing Innovation Institute to advance the use of additive manufacturing in aerospace.
- Lockheed Martin employs additive manufacturing for prototyping, tooling, and creating complex geometries in their components. Lockheed Martin has also invested in research and development initiatives to get more out of 3D printing in the future.
- Prodways Technologies is a joint venture between Boeing and Safran which focuses on developing additive manufacturing processes for aerospace applications. They aim to develop industrial-grade 3D printers capable of producing large-scale structural aircraft components using high-performance polymers.
What Will Be the Impact of 3D Printing in the Aircraft Industry's Future?
3D printing is expected to be transformative to aircraft design, manufacture, and maintenance. By its nature, 3D printing encourages innovation in aircraft design. This enables engineers to explore novel concepts, improve aerodynamics, and enhance performance. The ability to create customized components tailored to specific needs opens up new avenues for innovation. 3D printing also offers the potential for improved efficiency and cost reduction by streamlining manufacturing processes, reducing material waste, and enabling on-demand production. Finally, 3D printing allows for the production of lightweight, yet robust components that meet stringent performance and safety requirements.
Can 3D Printing Minimize the Aircraft Industry's Overhead Costs?
Yes, 3D printing technology has the potential to minimize the overhead costs in the aircraft industry in different ways. Firstly, it reduces tooling costs as it eliminates or reduces the need for expensive specialized tools, molds, and fixtures. Secondly, it enables the on-demand production of parts, reducing the need for large inventories and the associated costs of storage, logistics, and potential obsolescence. Additionally, 3D printing simplifies the complex supply chain in the aircraft industry. Consolidating multiple parts into a single 3D-printed component reduces the number of suppliers involved and streamlines the supply chain.
How Xometry Can Help
Xometry has services that are extremely applicable to the aerospace and aircraft industry, including 3D printing and an entire library of 3D printing design guides. We even have an entire section dedicated to manufacturing help for the aerospace and defense industries, providing companies with the services and connections they need. Get your instant quote today.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.