When comparing Inventor® vs Fusion 360®, it’s important to consider the different functions of each software. Both are computer aided design programs, but they differ in complexity, and usability.
Inventor is a professional, desktop-only CAD platform built for detailed mechanical design and complex assemblies, and is more traditional in its interface. Fusion 360 is a cloud-connected, all-in-one platform combining CAD, CAM, CAE, and ECAD, aimed at versatility and collaboration.
When it comes to digital prototyping, Inventor offers greater precision and realism, making it ideal for complex mechanical assemblies and high-tolerance engineering work. It’s the tool of choice for industries requiring exacting standards and detailed technical documentation.
Fusion 360, on the other hand, is designed to be more flexible, intuitive, and accessible, with integrated CAD, CAM, CAE, and electronics tools in a single platform. It’s ideal for startups, makers, and teams focused on product development and prototyping.
While Inventor is more expensive, Fusion 360 provides free and affordable options for individuals and small teams. Both software programs are very capable for users wishing to design models for 3D printing, although Fusion 360 has some tools for Additive Manufacturing not found in Inventor.
What is Inventor?
Inventor is a software program made by Autodesk® that is used for 3D mechanical design, documentation, and simulation. The company provides annual updates with new features and enhancements added with each release. Inventor is used by engineers and designers to create and refine three-dimensional models of physical objects. These objects can then be used in simulations to test their performance, or they can be constructed using a 3D printer or other manufacturing methods. Inventor is frequently used in the automotive and aerospace industries, as well as in other areas where precision and accuracy are essential.
What is Fusion 360?
Another Autodesk® product, Fusion 360 is a powerful 3D CAD, CAM, and CAE tool that enables engineers and designers to quickly turn their ideas into products. It helps you get from concept to fabrication faster thanks to an intuitive user interface and integrated workflows.
Fusion 360 enables you to design, simulate, and fabricate your products in a single program. The software combines parametric modeling with freeform 3D sculpting and solid modeling to give you the freedom to explore your ideas and create complex designs. With its integrated simulation and analysis tools, Fusion 360 helps you optimize your designs for manufacturability and performance.
Fusion 360 also has a Generative Design feature, which can be accessed by purchasing cloud credits. This feature uses artificial intelligence to create multiple, geometrically optimized designs for the user to select from.
For those wishing to design models for 3D printing, Fusion 360 allows for mesh editing, and also has an integrated slicer, which gives it an edge over Inventor for additive manufacturing tasks.
Inventor vs. Fusion 360 - Use Cases and Applications
Inventor is used by engineers and product designers to create prototypes, illustrations, simulations, and animations of their products. Fusion 360, on the other hand, can perform similar tasks but with a broader scope of integrated cloud-based collaboration than the more advanced, specialized and feature-rich Inventor. Fusion 360's use cases include sculpting, parametric modeling, generative design, and CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), among other capabilities.
Fusion 360 is used mostly in the product design, prototyping, and small-scale manufacturing fields for creating three-dimensional models, while Inventor is primarily favored for detailed mechanical engineering tasks and complex simulations. Both platforms allow modeling for export as mesh files, making them excellent for 3D printing. However, Fusion 360 features mesh editing capabilities for those who wish to modify existing STL files rather than create their own.
Inventor vs. Fusion 360 - System Requirements
The system requirements for Inventor are as follows:
- Operating System: Windows® 10 64-bit or Windows® 11 64-bit
- CPU: Intel® or AMD processor with 64-bit support
- RAM: 8 GB, 16 GB, and 32 GB + RAM (depending on project complexity)
- Storage: 40 GB + for installation
- Graphics Card: DirectX 11 compliant
- Browser: Google Chrome™ or equivalent
Fusion 360, on the other hand, has the following system requirements:
- Operating System: Windows 10 or 11 (64-bit), macOS 12 Monterey or later
- CPU: 4+ core processor, 3 GHz minimum
- RAM: 8 GB of RAM
- Storage: 5 GB available space
- Graphics Card: DirectX 11.0 compatible, 2GB video memory recommended
- Browser: Latest version of Microsoft® Edge, Safari, Google Chrome, or Firefox
What is the Operating System of Inventor and Fusion 360?
Inventor is only compatible with the Windows® operating system, while Fusion 360 is compatible with both Windows® and macOS®. This compatibility makes Fusion 360 a more versatile program for users who want to use it on either type of computer.
What Are the Minimum Memory Requirements for Inventor and Fusion 360?
To run Inventor or Fusion 360 smoothly, your computer will need at least 8 GB of RAM. If you have a computer with less than 8 GB of RAM, you may experience performance issues such as slow rendering times and lagging. For the best possible experience, 8 GB of RAM or more is recommended. It is also important to have a processor that is capable of handling the software (at least a 3rd-generation Intel Core i5 processor or equivalent).
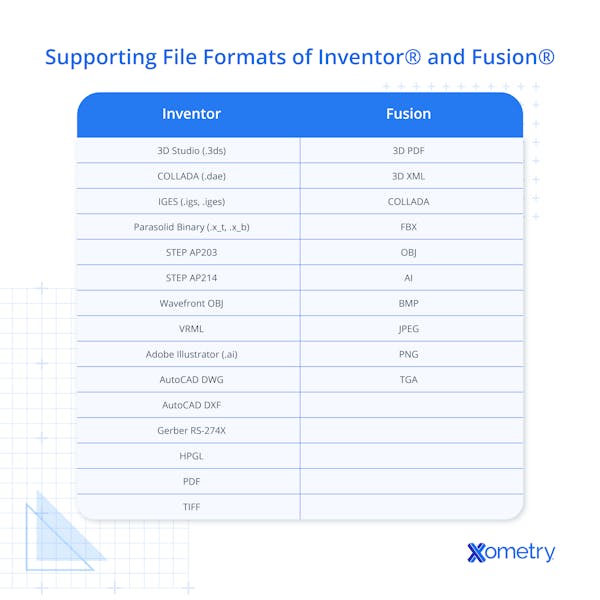
What File Formats Do Inventor and Fusion 360 Support?
Both Inventor and Fusion 360 have their own respective native files that can be imported and exported, as seen in the table below.
In addition, both software programs can use a range of CAD neutral formats such as STEP, IGES, and Parasolid. They can both export as various mesh-based files such as STL, OBJ and 3MF.
Inventor vs. Fusion 360 - User Experience
Due to Inventor’s complexity, its user experience is not as streamlined as that of Fusion 360. Inventor has enough features and options to make it overwhelming for users who are not familiar with similar software. By contrast, Fusion 360 is much more user-friendly and intuitive.
Learning Curve of Inventor and Fusion 360
The learning curve for both Inventor and Fusion 360 can be quite steep, but it is generally milder for the latter. With a little bit of patience and perseverance, it is possible to become proficient in both programs. In terms of which program is easier to learn, it depends on the individual. In general, Fusion 360 tends to be more user-friendly and has a more intuitive interface. Inventor, on the other hand, is more powerful and can be used to create more complex designs. Ultimately, every user’s experience comes down to personal preference and their aims for the software.
Is Inventor Easier to Learn and Use Than Fusion 360?
This is subjective and can depend on what you are used to. If you have previous experience in parametric CAD programs, you might find Inventor more familiar in terms of how it works. Conversely, if you have no background in CAD or 3D modelling, you might find Fusion 360 easier to work with due to its intuitive design, user-friendly GUI, and workflows.
Inventor is a parametric modeling application with more powerful assembly and modeling features. Fusion 360 is a direct modeling application that can be more intuitive for beginners but can also be used for parametric modelling for those wanting a more constraint-based workflow. Fusion 360 can be faster and easier for some users to learn, while experienced users may find Inventor's constraint-based modeling approach more intuitive.
Inventor vs. Fusion 360 - Application Stability
When it comes to lag, crashes, and latency, both Inventor and Fusion 360 do not suffer excessively. Lag is the delay between when you input a command and when it's executed by the software. Latency typically refers to delays due to network or cloud processing, especially relevant for Fusion 360's cloud-based operations. Lag and latency can both be frustrating when working on complex designs, but having the recommended amount of RAM and correct CPU can help mitigate many of these issues.
Crashes can also be a problem with any software, but they're especially costly in CAD applications. If your computer software crashes while working on a design, you may lose all of your unsaved work.
However, both applications are improving in these areas, and as of now, there isn't a clear winner. In the end, your decision depends on your needs and which application is more stable for you.
Inventor vs. Fusion 360 - Customer Support
Inventor and Fusion 360 are both Autodesk® products, and users may contact customer support to resolve product-related issues. Customers can choose from phone support, email support, or web support from customer care personnel.
Inventor vs. Fusion 360 - Community
Fusion 360 and Inventor both offer community support, with the latter more geared toward professionals. In addition to Autodesk® resources, there are numerous online forums for users who want to talk about issues or ideas.
Inventor vs. Fusion 360 - Price
Inventor is a premium, feature-rich CAD solution with higher pricing tiers, suitable for complex mechanical designs and simulations.
Fusion 360 offers a more affordable, cloud-based solution with integrated CAD, CAM, CAE, and PCB tools, ideal for startups, hobbyists, and small businesses.
The price of the commercial versions of each software is shown in the table below. It should be noted that there are free educational licenses available to students, and there may be discounts available for startups.
| Software | Monthly Subscription | Annual Subscription | 3-Year Subscription |
|---|---|---|---|
Software Inventor | Monthly Subscription $320/month | Annual Subscription $2,585/year | 3-Year Subscription $7,885.99 |
Software Fusion 360 | Monthly Subscription $85/month | Annual Subscription $680/year | 3-Year Subscription $2,040 |
Disclaimer: Prices were verified in May 2025.
Other Alternatives to Inventor and Fusion 360
Other alternatives to Inventor and Fusion 360 are CATIA, Solidworks®, and PTC Creo. Each piece of software has its advantages and disadvantages. It is important to choose the software that best matches your needs. CATIA, for example, is very powerful CAD software with strong surface modelling capabilities, but can be difficult to learn (and costly). Solidworks® is a popular choice for many engineers and designers and is especially good for solid modeling (although surface modeling is available too). PTC Creo features both surface and solid modelling, and is especially good at handling large assemblies.
Summary
This article presented Inventor and Fusion, explained what they are, and discussed each software is used for 3D printing. To learn more about 3D printing software, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including 3D printing and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Copyright and Trademark Notices
- SolidWorks® is a registered trademark of Dassault Systèmes SolidWorks Corp.
- Autodesk®, Fusion®, and Inventor® are trademarks of Autodesk, Inc., and/or its subsidiaries and/or affiliates, in the United States.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


