There has been some debate over what the acronym for the STL file format actually stands for. Since the early days of 3D printing, several interpretations (or backronyms) have been associated with STL. It is commonly referred to as "Stereolithography," "Standard Tessellation Language," or "Standard Triangle Language." All these definitions are widely accepted and accurately describe the format’s function, reflecting either its origin or the geometric structure used in 3D printing and CAD software.
An STL file defines the geometrical surface of 3D models using a mesh of triangular facets. These triangles collectively approximate the shape of the object by covering its surface, much like how a tiler covers a floor with tiles. This process is known as tessellation, which refers to the division of a surface into a network of contiguous triangles without gaps or overlaps. Numerous software applications are available for creating, viewing, or editing STL files, depending on the specific needs of the user. Tools such as Autodesk Fusion 360 and SketchUp support STL workflows, allowing users to design 3D models and export or import them in STL format for 3D printing or further processing.
This article will discuss the STL file format, including its definition, the types of STL files, its history, and converters.

What Are STL Files?
STL files interpret the geometrical surfaces of 3D models created with the help of CAD software. Though other file formats exist, the STL format is simple to understand and use. STL files describe, interpret, or encode these surfaces using a series of small triangles, known as tessellation or tiling. The complexity of the models or designs is proportional to the number of triangles used and the resolution of the 3D image. In addition, 3D STL files work hand-in-hand with the slicer software to bring the job of 3D printers to reality.
Who Created the STL File Format?
The STL (Standard Tessellation Language or Standard Triangle Language) file format was introduced in 1987 by 3D Systems, under the direction of Chuck Hull, the company's co-founder and then-president. Chuck Hull is also credited with inventing stereolithography (SLA), a foundational 3D printing technology that uses a UV-sensitive resin cured layer-by-layer to produce solid objects. STL files were initially developed to support this stereolithography process by providing a digital representation of an object's surface geometry. The file format encodes the geometry using a mesh of triangles that defines the outer shell of the 3D model, excluding color, texture, and material information. Since its inception, the STL format has remained essentially unchanged and continues to serve as a widely accepted standard in 3D printing workflows, especially for rapid prototyping and additive manufacturing.
How to Convert an STL File in FreeCAD
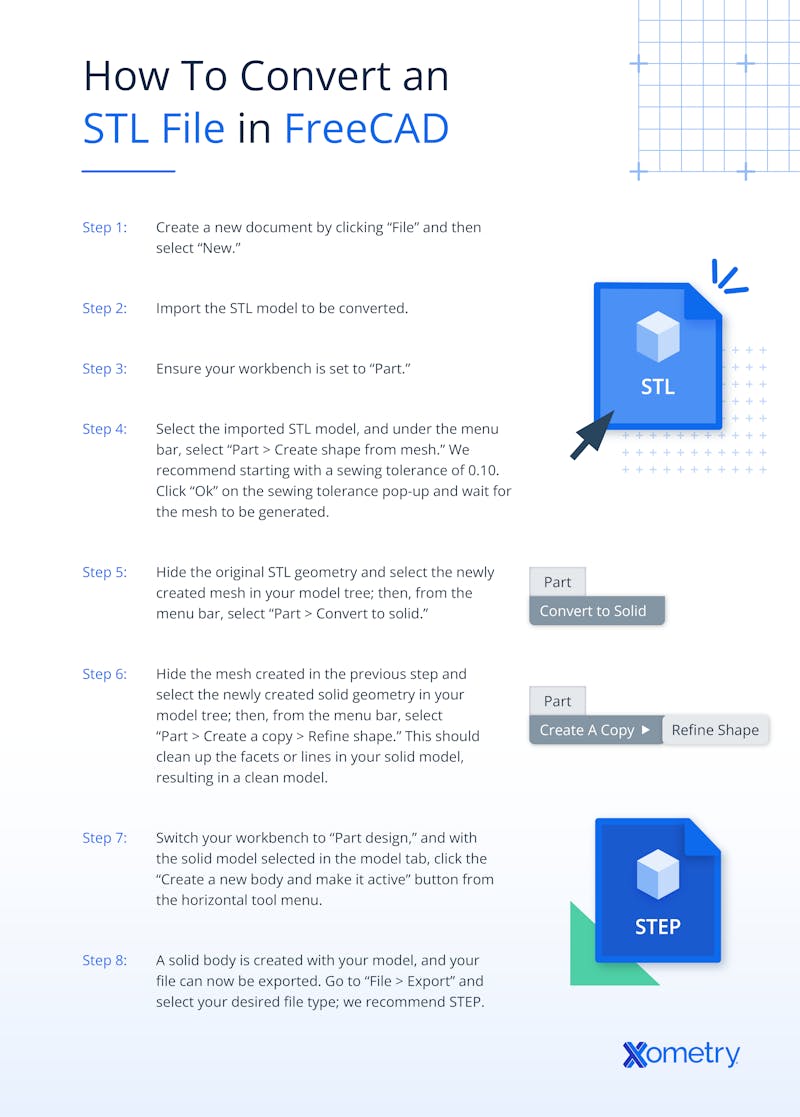
The steps in converting an STL file depend on the software or online tool used. It is essential to follow the specific software or tool instructions. For STL file conversion to a solid or CAD model, the following steps can be followed:
- Create a new document by clicking “File” and then selecting “New.”
- Import the STL model to be converted.
- Ensure your workbench is set to “Part.”
- Select the imported STL model, then go to the menu bar and choose: (1) Part → Create shape from mesh. (2) A pop-up will prompt you to set a sewing tolerance; a value of 0.10 is typically recommended (3) Click OK and wait for the mesh shape to be generated.
- Hide the original STL geometry and select the newly created mesh in your model tree; then, from the menu bar, select “Part → Convert to solid.”
- Hide the mesh created in the previous step and select the newly created solid geometry in your model tree; then, from the menu bar, select “Part → Create a copy → Refine shape.” This should clean up the facets or lines in your solid model, resulting in a clean model.
- Switch your workbench to “Part design,” and with the solid model selected in the model tab, click the “Create a new body and make it active” button from the horizontal tool menu.
- You now have a fully defined solid body based on the original STL mesh. To export the model, go to File → Export, and select your preferred CAD file format.
STEP (.step/.stp) is recommended for high interoperability with other CAD systems.
For more information, see our guide on how to Convert an STL File to a STEP File.
How Do I Open an STL File?
There are many ways of opening the STL file format, depending on the software or tool used. The process of opening an STL file below uses Autodesk Fusion:
- Go to the insert menu found on the design workspace and select the Insert Mesh command.
- A dialogue will open. Select the STL or mesh file.
- Select the unit type and place the model as needed.
- Orient the model as required.
It is important to note that uploading the STL or mesh file to the data panel of Fusion should be avoided. This will make reorienting the model impossible. Always import it through the Insert Mesh command.
How Can I Make an STL File?
An STL file can be created by following the steps below.
1. Open TinkerCad or SketchUp, Depending on Your CAD Application of Choice
Creating an STL file starts with CAD software, which offers many options. There are STL files made just for beginners and those made for professionals. Depending on one's level of expertise, there is a variety of STL files to suit one's needs. Starters or beginners can go for TinkerCad or SketchUp because of their relatively simple, user-friendly interfaces. Engineers and artists alike may go for Autodesk Inventor and Blender, respectively. While some programs require payments, TinkerCad and SketchUp are free. All the user needs to do is to create an account and start – straight up – though after a good understanding of either program’s functionality.
2. Create the Model or Design
Once a suitable software application is downloaded, prepare the workspace. Check and familiarize yourself with the tools provided. Some tools, when misused, show an error message. With the chosen tool, an axis can be sketched and a basic 2D model drawn. It must be noted that understanding and accepting the terms and conditions of the software's cookies ensures a complete and enhanced experience.
3. Save and Export Your Design to Your Computer
The STL file created on the CAD software can easily be exported to the computer through the autosave feature. With this, downloading becomes unnecessary. Its purpose is also to ensure that the work remains intact. Exporting a 3D printer STL is not difficult. Locate "export" on the software's page and click on it. A box should pop up containing several options. Most software will present the user with any of these: standard triangle language, standard tessellation language, or stereolithography. They are all valid and should be chosen as the case may be.
It is important to note that all these conditions must be satisfied before exporting the file for the best result:
- Check the file or model for uniformity
- Check for holes in the mesh part
- Alter the dimensions or adjust the scale if so desired
4. Select a Slicer Program
Compared to other slicer programs, Cura is beginner-friendly and features a navigable graphical user interface (GUI) developed by Ultimaker. It is popular among both beginners and professionals. Its function is to slice a 3D model STL file and translate it to a form that the 3D printer can interpret.
5. Open the File and "Slice" it to a G-code File
G-code is a language the printer can understand and process. This is where the slicer software comes in. It transforms the STL files into a form the computer can understand.
What is the Importance of an STL File?
An STL file plays a critical role as an intermediary between CAD models and 3D printing hardware. The STL format represents the surface geometry of a 3D object using a mesh of triangular facets, allowing the slicer to generate toolpaths and instructions (G-code) for additive manufacturing. While several other file formats are available, STL remains the most widely supported and commonly used format in both professional and consumer 3D printing workflows. Due to its widespread compatibility and simplicity, STL is often considered the standard file format for rapid prototyping and 3D printing, especially when color, texture, or material data are not required.
Frequently Asked Questions About STL Files
What are the Types of STL Files?
There are two types of STL files: ASCII and binary STL. They are both used in encoding information about geometrical surfaces that have been triangulated or tessellated. Information is stored in both cases as the vertex coordinates and the unit normal vector components to the triangle. In most cases, it should be enough to use ASCII. But complex designs – those tiled with many small triangles – work best with the more compact binary STL file format.
What are the Best STL File Converters?
Several tools are available for converting STL files to and from other formats, depending on the desired workflow and file types involved. Below are some of the most effective STL file converters:
- Meshconvert: This is a dedicated tool for converting mesh-based geometry. It supports a wide range of formats commonly used in 3D printing and computer graphics. Meshconvert is free, but it is intended only for mesh files—not for solid models or parametric geometry. It is ideal for converting between formats like STL, OBJ, and PLY.
- Online CAD Converter: This is a commercial conversion tool that supports an extensive range of file formats, including both mesh and solid geometry formats. In addition to standard graphics formats, it can handle ASM (Pro/ENGINEER/Creo) and IPT (Autodesk Inventor) files. Users can convert one file for free, but multiple or batch conversions require a paid subscription. It’s a suitable option for professional workflows involving proprietary CAD files.
- Greentoken: Greentoken is a free online converter known for its broad file format support, covering both neutral (e.g., STEP, IGES) and proprietary formats. It stands out among free converters because of the wide variety of input types it accepts. While it lacks advanced editing features, its flexibility and no-cost access make it an excellent choice for quick conversions.
What are the Best Applications for STL files?
STL files are widely used in 3D printing, mesh editing, and digital sculpting workflows. Several applications support STL file viewing, editing, or preparation, depending on the specific use case.
- MeshLab: MeshLab is a powerful open-source tool designed for working with triangular meshes. It provides a suite of features for inspecting, cleaning, editing, and converting STL files. This makes it especially useful for processing raw scan data or exported geometry before sending it to a 3D printer. It supports advanced mesh optimization, repair, and analysis functions.
- SketchUp: SketchUp is a user-friendly 3D modeling application commonly used in architectural design, landscape planning, and conceptual modeling. With the use of STL import/export extensions, SketchUp can serve as a valuable tool for creating and modifying models intended for 3D printing.
- SculptGL: SculptGL is a lightweight, browser-based sculpting tool ideal for quickly creating or modifying organic shapes. It functions like a digital clay tool, allowing users to push, pinch, smooth, and mold geometry into 3D forms. While it lacks the advanced features found in professional sculpting software, SculptGL is an accessible entry point for creating STL models, offering intuitive controls and eliminating the need for software installation.
Is an STL File the Same as a CAD File?
No, an STL file is not the same as a CAD file. CAD files are used to create 3D models, while STL files are created by tiling or tessellating the models' geometrical surfaces with triangles. Put another way, an STL file is an approximated version of the CAD file.
Summary
This article presented STL files, explained them, and discussed their origin and how to create them. To learn more about STL files, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including 3D printing and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


