Both injection molding and compression molding are considered traditional methods of making plastic parts. They both rely on heat and pressure but use different approaches to shaping the materials. So what’s so different about them, and when would you use either one? Let’s find out.
Injection Molding Definition and Comparison to Compression Molding
The injection molding process involves injecting molten thermoplastic into a mold cavity. The machine melts the plastic resin pellets inside its heated barrel, then a screw inside turns, forces, and compresses the pellets forward into smaller spaces at high pressure. The screw itself isn’t heated, but the mechanical force it generates, along with the heat from the barrel, is enough to keep the plastic in melted form. The following image gives you an idea of what a simple setup looks like:
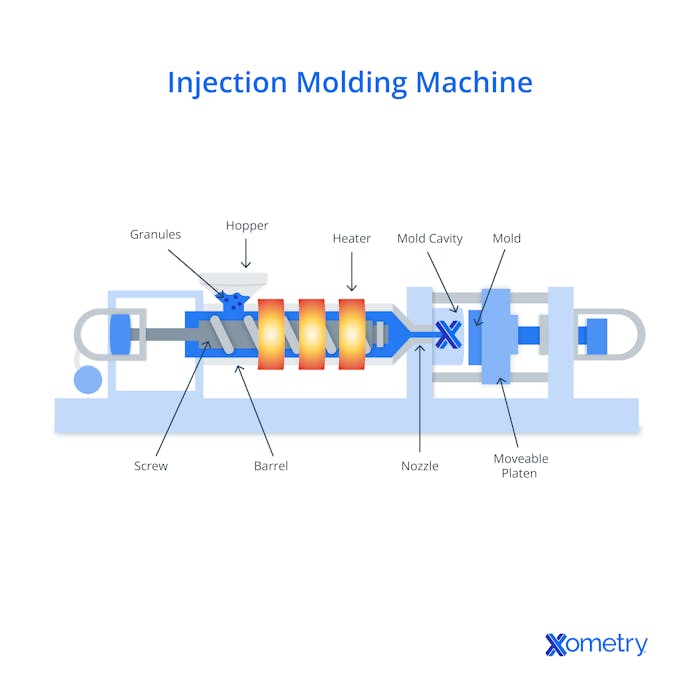
The process hasn’t changed much since the first screw injection molding machine was developed by an American inventor named James Watson Hendry in 1946, and most modern equipment is still based on his design. Hendry’s design was based on the design of the first injection machine made in 1872 by another inventor from the U.S., John Wesley Hyatt. But this didn’t have an advanced screw mechanism.
The mold typically has two parts (sometimes more) that are held in place by hydraulic rams so that no plastic can escape through the cracks. There are also cooling channels that help the plastic harden before it’s time to take it out to avoid it getting damaged. You’d be hard-pressed to find another method as effective for mass production; it can tackle huge runs – we’re talking millions of parts per machine per year.
This method has another advantage, too: it’s highly automated and very fast, which ultimately makes its parts relatively cheap. Some of the potential drawbacks, though, include the fact that the mold needs to be able to withstand the high pressure, so tooling could work out a little more expensive. Also, for large, thin parts like vehicle panels, you’re probably better off using a different manufacturing technique.
What are the Advantages of Injection Molding Compared to Compression Molding?
Listed below are some advantages of injection molding compared with compression molding:
- Injection molding is a high-volume production method that can produce millions of parts per machine annually.
- Due to the high levels of automation and rapid manufacturing speed, injection molded parts are cheaper than compression molded parts.
What are the Disadvantages of Injection Molding Compared to Compression Molding?
Listed below are some disadvantages of injection molding compared with compression molding:
- Injection molding requires very high plastic injection pressures. The mold must therefore be built to withstand these high pressures. This adds cost to the tooling.
- Injection molding is not well suited to the manufacture of large, thin parts like vehicle panels.
Compression Molding Definition and Comparison to Injection Molding
Considered one of the most popular ways of creating parts from pliable materials, compression molding was first developed in 1905 as a way of making bakelite components. This type of molding usually uses a two-part mold, with the bottom part securely attached to the base of the tool and the top half free to move up and down. They’re generally heated to help cure the piece (sometimes called the charge) and get it ready for compression. The charge is weighed and placed inside the bottom half of the mold before the top half moves down and squeezes it into shape. The heated mold then stays closed for a few minutes to allow the charge inside to cure. After that, the part is removed and moved to post-processing, where any flash (excess material that builds up at the parting line) is removed. This is really common when it comes to compression molded parts.
This process is used extensively to create reinforced panels. For instance, fiber-filled plastic sheets are laid out in the bottom half of the mold, and when the top half compresses the material to take its shape, it creates a composite part. That’s how large plastic car bumpers are made. You can read our guide on compression molding to dig a little deeper.
Compression molding has lots going for it. For example, it can use SMC (sheet molding compound) and BMC (bulk molding compound) to make composite panels. Instead of having a continuous string of fiber running through them, they have chopped strands that are distributed throughout the bulk material. Other processes, like injection molding, can’t make composite parts. Another advantage is that compression molding can work out a bit cheaper because it doesn’t rely on extreme internal pressure. The downsides? It’s not the fastest procedure out there, and it can’t really make highly complex parts. That’s because the materials tend to be rather viscous and won’t flow very well into tiny little cavities to make intricate designs. The following image further illustrates how this works:
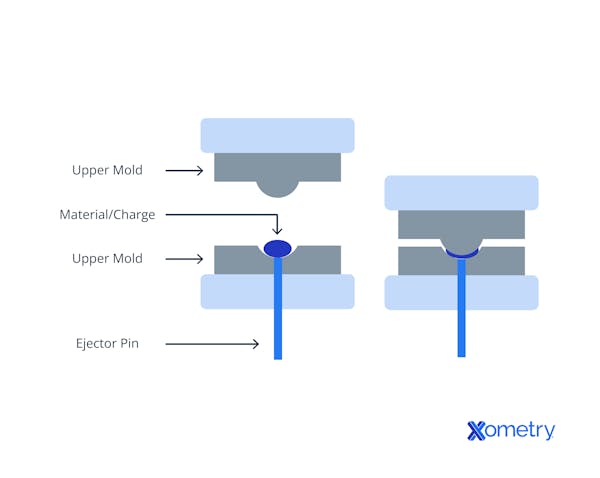
What are the Advantages of Compression Molding Compared to Injection Molding?
Listed below are some advantages of compression molding compared to injection molding:
- Compression molding can make use of SMC (Sheet Molding Compound) and BMC (Bulk Molding Compound) to create composite panels. These panels do not have continuous fiber-impregnated sheets, but rather chopped fiber strands that are distributed throughout the bulk material. The injection molding process cannot make composite material parts.
- Compression molds do not need to withstand high internal pressures as do injection molds. Instead, the only load they experience is a compression force from above. This means that compression molds tend to be less expensive.
What are the Disadvantages of Compression Molding Compared to Injection Molding?
Listed below are some disadvantages of compression molding compared to injection molding:
- Compression molding is a very manual and slow process. Even if a robot arm is used to add the charge and remove the product, the cycle time between parts is still much slower than injection molding due to the need for the parts to be set before being removed.
- Compression molding cannot create parts with high levels of complexity. The materials used are typically very viscous and as a result, they don’t flow well into small, complicated features.
Comparison Table Between Injection Molding and Compression Molding
Attributes of compression molding vs. injection molding are shown in Table 1 below:
| Attribute | Injection Molding | Compression Molding |
|---|---|---|
Attribute High-volume production process | Injection Molding Yes | Compression Molding No |
Attribute Materials | Injection Molding Thermosets, thermoplastics (including fiber and metal-filled), thermoplastic elastomers, metal-filled polymers, fiber-filled thermoplastics | Compression Molding Thermosets, thermoplastics, silicone, unvulcanized rubber, BMC, SMC |
Attribute High tooling cost | Injection Molding Yes | Compression Molding No |
Attribute Can produce large, thin-walled panels | Injection Molding No | Compression Molding Yes |
Attribute Post-processing required | Injection Molding TRUE | Compression Molding TRUE |
Injection molding is better suited to high volume production whereas compression molding is better suited to pliable and flexible materials. Compression molding also has cheaper tooling costs.
Injection Molding vs. Compression Molding: Lead Cost Comparison
When it comes to individual part cost, injection molding can produce inexpensive, complex parts. However, this process is only cost-competitive if production run volumes are large enough to spread the high cost of injection molding tooling over a sufficient number of pieces. At lower volumes, compression molding is cheaper than injection molding due to the lower initial mold costs.
Injection Molding vs. Compression Molding: Speed Comparison
Injection molding is significantly faster than compression molding. The cycle time for injection molded parts can be a few seconds, whereas compression molding cycle times can easily reach a few minutes. This is because compression molded parts often need to cure before they are removed from the mold.
Injection Molding vs. Compression Molding: Volume Comparison
Injection molding is a high-volume production method that is unmatched by any other manufacturing technology. Injection molding processes can be fully automated, while compression molding often requires a person to place the material into the mold, remove it, and post-process it.
Injection Molding vs. Compression Molding: Materials Comparison
Injection molded parts can be manufactured from. The process can make use of rigid thermoplastics as well as thermoplastic elastomers and thermoplastic urethanes. Compression molding more often makes use of flexible elastomers like rubber and silicone, but can also produce rigid composite components by making use of SMC and BMC.
Frequently Asked Questions on Injection and Compression Molding
What Are the Mutual Alternatives to Injection Molding and Compression Molding?
The closest is probably transfer molding. It has certain characteristics of both and works by pressure-forcing the material into an enclosed mold. Sometimes, the material is actually solid but melts because of the pressure. Transfer molding is fine to be used with materials like rubber, silicone, and even normal thermoplastics.
What are the Similarities Between Injection Molding and Compression Molding?
Listed below are some similarities between injection molding and compression molding:
- Injection molding and compression molding can both produce plastic parts.
- Compression molding and injection molding both make use of heat and pressure to produce plastic parts, albeit with different mechanisms.
What are the Other Comparisons for Injection Molding Besides Compression Molding?
Below is an alternative to injection molding:
- Injection Molding vs. Blow Molding: Blow molding is another high-volume production technology that transforms thermoplastics into products. Blow molding, however, is specifically suited to the manufacture of thin-walled, hollow containers.
What are the Other Comparisons for Compression Molding Besides Injection Molding?
Below is an alternative to compression molding:
- Compression Molding vs. Urethane Casting: Urethane casting is a low-volume production method for producing parts. Casting in the plastics industry typically refers to the casting of polyurethane or nylons. The process involves pouring a liquid thermosetting polymer into a mold under atmospheric pressure to produce parts. The thermosetting polymer will then cure in the mold before it can be removed. Casting is capable of producing parts with fine features.
How Xometry Can Help
If you want to know anything else about molding or other manufacturing techniques, you can reach out to one of our representatives who would be happy to help. Xometry also offers a huge range of related services including injection molding, compression molding, CNC machining, and 3D printing. Why not request a free, no-obligation quote on our website and get your project started right away?
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.