A36 is a low-carbon, mild steel that was formulated by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) to be strong and tough so it can be used in structural applications, like buildings and bridges. It’s a common go-to in heavy machinery, automotive, and oil and gas. It’s also affordable! Let’s have a look at exactly what it’s made up of, how it’s made, and the various forms it comes in.
What is A36 Carbon Steel?
On A36’s resume, under strengths, you’ll find hardness, ductility, formability, and malleability, among others. Whether you need to put it through welding, punching, grinding, drilling, tapping, or machining, A36 will oblige without a complaint. In addition to all those benefits, A36 is a good magnetic field conductor because it’s paramagnetic (only slightly attracted to magnets), and it won’t let any electromagnetic waves get through, either. With all these perks, it’s little wonder that A36 is the most commonly used carbon steel in its category.
As well as iron and carbon, A36 has various other elements that give it all these wonderful properties. It consists of iron with manganese and carbon as the main alloying elements, and smaller amounts of silicon, copper, sulfur, and phosphorus (we’ll tell you the exact amounts of each a little further down). It’s made in much the same way as other carbon steels; the molten metals are mixed together and then hot rolled. Before the alloying elements are added, the iron ore is first melted in a coal furnace to burn the impurities away. After the other ingredients are thrown in, the molten mixture is put into ingots and left to harden before the hot rolling step of the process.
Its low carbon content makes it quite the task to figure out exactly how much carbon is in every batch made (but we’ve got a good formula for that below). It’s also quite heavy with a low strength-to-weight ratio, and it’s not particularly corrosion resistant (you can thank the lack of nickel and chromium in its composition for that).

What Is A36 Carbon Steel Used For?
A36 carbon steel is a material with a wide scope of applications due to its low cost and wide range of desirable properties including: weldability, formability, strength, and toughness. Most applications for A36 steel are structural such as in bridges and buildings. A36 steel also finds applications in the automotive, construction, heavy machinery, and oil & gas industries.
How Is A36 Carbon Steel Made?
A36 carbon steel is made by mixing the molten metals together and then hot rolling them. This process is similar to most carbon steels, and the only real difference is the chemical composition.
The first step is melting iron ore in a furnace with coal and then burning away the impurities. Next, the alloying elements including manganese and carbon are added. The molten metal is solidified into ingots before finally being hot rolled. Hot rolling is a process in which ingots are rolled into a final dimension at an elevated temperature.
What Is the Chemical Composition of A36 Carbon Steel?
As promised, you can see the breakdown of A36’s contents in the below table, and just under that, how you can calculate the exact carbon content.
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
Element Iron | Percentage 98% |
Element Manganese | Percentage 1.03% |
Element Carbon | Percentage 0.25%–0.29% |
Element Silicon | Percentage 0.28% |
Element Copper | Percentage 0.20% |
Element Sulfur | Percentage 0.05% |
Element Phosphorous | Percentage 0.04% |
Table 1: Chemical Composition of A36 Carbon Steel
What Is the Carbon Content of A36 Carbon Steel?
The carbon content of A36 steel is 0.25%–0.29%. Steels less than 0.3% carbon are considered low-carbon steels. Low-carbon steels are renowned for their ductility, malleability, and weldability. However, they have a lower strength-to-weight ratio and less corrosion resistance than high-carbon steels.
Is A36 a Low-Carbon Steel?
Yes, A36 is low-carbon steel as it has less than 0.3% but more than 0.05% carbon by weight. A36 is a very popular low-carbon steel. Other popular low-carbon steels created by ASTM are A572 Grades 42 and 50 as well as A830-1020.
How To Calculate Volume Fraction of Carbon in A36 Steel?
To calculate the volume fraction of carbon in A36 steel, you have to divide the volume of the carbon by the volume of all of the other elements. Here’s the formula:
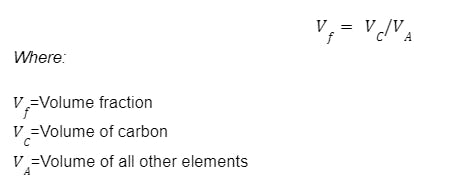
Volume fraction formula.
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
Property Density | Value 2.84 lb/in^3 |
Property Yield strength | Value 36,259 psi |
Property Hardness | Value 67–83 Rockwell |
Property Magnetism | Value Ferrous magnetic |
Property Machinability | Value 72% |
Property Cutting speed | Value 120 ft. per minute |
Property Melting point | Value Between 2,590–2,670°F |
Property Specific heat capacity | Value 0.11 Btu/lb 348 Btu-in/hr-ft2 F |
Property Thermal conductivity | Value 348 Btu-in/hr-ft2 F |
Table 2: Properties of A36 Carbon Steel
Machinability Rating of A36 Carbon Steel
The machinability rating of A36 steel is 72% machinable. The average cutting speed of A36 steel is 120 ft per minute. While this is a good rating, it is not as easy to machine as 1018 and may be a reason to choose 1018 vs. A36.
What Are the Thermal Properties of A36 Carbon Steel?
A36 carbon steel has a melting point in the range of 2,590–2,670 °F. It also has a specific heat capacity of 0.11 Btu/lb Fahrenheit and a thermal conductivity of 348 Btu-in/hr-ft2 F.
What Are the Uses of A36 Carbon Steel?
A36 carbon steel is used for a wide variety of applications as it has a versatile range of properties including good hardness, strength, malleability, weldability, ductility, and machinability. These properties, coupled with their low cost, cause A36 steel to be widely used in structural applications, especially in the civil construction industry to build buildings and bridges. A36 steel is also used in the automotive, construction, heavy machinery, and oil & gas industries.
What Are the Common Forms of A36 Carbon Steel Material?
These are the common forms that ASTM A36 carbon steel can be found in and how they’re used.
Sheet
This is between 0.018” and 0.250” thick and used for vehicle bodywork, walls/bulkheads, or build tanks.
Bar
These are used in structural applications, like concrete reinforcement, because concrete has a high compressive strength and a low tensile strength.
Plate
Similar to sheets, plates are 0.25” or more in thickness, but are used for structural applications (whereas sheets just look pretty).
Hot-rolled
This is the most common form and creates a rougher surface finish. It’s done at really high temperatures (1,562–2,192°F), and puts strain on the steel to ramp up the dislocation density of the steel’s microstructure. This results in work hardening and creates grain elongation (stretching out the tiny grains that make up the metal).
Annealed
This also uses high heat of 1,550–1,600°F and involves heating and then cooling the steel slowly to remove impurities and make it less brittle. The process reduces the steel’s hardness but also helps reduce internal stress, making it less likely to cause damage to cutting or shaping tools.
Cold-drawn
Stronger and harder than hot-rolled steel, cold-drawn A36 is made at a lower temperature and can be made into bars, tubes, spindles, wires, shafts, and other items that need to have a nice aesthetic.
What Are the Advantages of Using A36 Carbon Steel?
The biggest advantage A36 carbon steel has is its versatility. It is applicable for a range of applications at a low cost. Some of A36’s main advantages are listed below:
- Easy to weld
- High strength
- Malleable
- Ductile
- Machinable
What Are the Disadvantages of Using A36 Carbon Steel?
A big limitation of A36 steel is its limited protection from corrosion. This is because this steel has no nickel or chromium added. Other disadvantages are listed below:
- Low strength-to-weight ratio
- Lower strength than similar 1018 steel
- Hard to accurately obtain its precise carbon content
What Are Equivalents Grades of A36 Carbon Steel?
While it’s difficult to exactly match A36 with the equivalent international standards (each will no doubt have a slightly different composition and properties), we list some comparable grades in the table below.
| Country standard | Equivalent grade |
|---|---|
Country standard European | Equivalent grade S235JRG2 |
Country standard German | Equivalent grade St 37-2 |
Country standard Canadian | Equivalent grade 260W |
Country standard Japanese | Equivalent grade SS400 |
Country standard Indian | Equivalent grade E250 |
Country standard Chinese | Equivalent grade Q235B |
Country standard ISO | Equivalent grade E 235 |
Table 3: Equivalent Grades of A36 Carbon Steel
What Is the Difference Between A36 Carbon Steel and 1018 Carbon Steel?
These two steels are quite similar, but 1018 has a lower carbon content (around 0.18%), is stronger, and more easily machinable. 1018 is great for rotating parts, but A36 is chosen for things like I-beams and cables. Since A36 is typically hot rolled, it’s cheaper to make than 1018, which is hot rolled and needs quite a lot of manual labor. If you need something economical and you’re not after super high strength and machinability, A36 is ideal. Otherwise, go with 1018.
What Is the Difference Between A36 Carbon Steel and A572 Steel?
ASTM carbon steels A36 and A572 have most of the same alloying elements, just in different amounts—something that changes some of the properties, i.e., yield and tensile strength. A572 has more manganese and silicon, which makes it stronger than A36 and able to bear more weight as it’s a high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steel.
How Xometry Can Help
We hope you enjoyed learning about A36 carbon steel and that we answered all your queries. To learn more about it, contact one of our reps. We also offer many related manufacturing services, and it’s easy to get a free and instant quote—simply upload your designs to the Xometry Instant Quoting Engine®.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.