Thermal resistance is an essential parameter in engineering, physics, thermodynamics, and even manufacturing. It plays an important role in the design and optimization of thermal systems, like electronic devices, insulation materials, and building envelopes. Here’s everything you need to know, including how to calculate it in every material.
What is Thermal Resistance?
A material or system’s ability to resist the transfer of heat, more precisely, the ratio of temperature difference to heat transfer rate, is referred to as its thermal resistance. This can also be described as the relationship between the temperature difference across a material and the rate of heat that’s flowing through it. Insulation materials used in construction should have high thermal resistance values because they reduce the speed of the heat transferred through the building envelope, helping to maintain interior temperature and improve energy efficiency. In contrast, heat exchangers and sinks need to be made from a material that has low thermal resistance because the aim is for heat to travel as easily and effectively as possible.
When it comes to manufacturing processes like plastic injection molding, 3D printing, and laser cutting, thermal resistance will dictate the material’s performance. The wrong thermal properties can lead to warping, cracking, or deformation. Low thermal resistance materials require slower laser cutting to prevent damage, while high resistance materials can withstand higher speeds with minimal or no distortion. In thermal management, it helps prevent overheating, improves energy efficiency, and enhances print quality. High thermal resistance materials also reduce energy costs, help keep temperatures stable indoors, and are even used in fireproofing applications.
A material’s thermal resistance is a bit tricky to accurately calculate because there’s no one-size-fits-all formula; it depends on the material’s thickness, surface area, and thermal conductivity. But don’t worry, we’ve got an easy-to-follow guide below with everything you need to do to work it out.
Christian Tsu-Raun, a Team Lead, Manual Quoting here at Xometry says "Thermal resistance is important because we live in a thermal environment. One of the key properties of plastics is that they are plastic — that is to say workable at low temperatures, not very far above environmental temperatures. This allows them to be extruded/injected/cast with minimum additional heating, reducing cost. However, this also means that possible ambient temperatures can cause parts to warp, shift, or deform more easily. Because of this, it is important to consider the thermal conditions the parts will be subject to, and choose a material that is able to withstand them."
Thermal resistance is important because we live in a thermal environment. One of the key properties of plastics is that they are plastic — that is to say workable at low temperatures, not very far above environmental temperatures. This allows them to be extruded/injected/cast with minimum additional heating, reducing cost.Christian Tsu-RaunTeam Lead, Manual Quoting
Affecting Factors
First, let’s have a look at a few things that could affect the thermal resistance of a material, and why.
Surface area: This influences the rate of heat transfer between the material and its surroundings, so it affects the thermal resistance. An increased surface area and lower thermal resistance can make the part more effective at transferring heat.
Porosity: Porous materials have a lower thermal conductivity than non-porous ones, even if it’s the same material, because trapped air reduces heat transfer. This is quite a major factor in insulation materials where high thermal resistance is needed.
Composition: Materials with poor thermal conductivity typically have a high thermal resistance.
Thickness: Thicker materials generally resist heat transfer better than thin ones. The precise relationship between thickness and thermal resistance ultimately depends on the material’s characteristics and the mode of heat transfer.
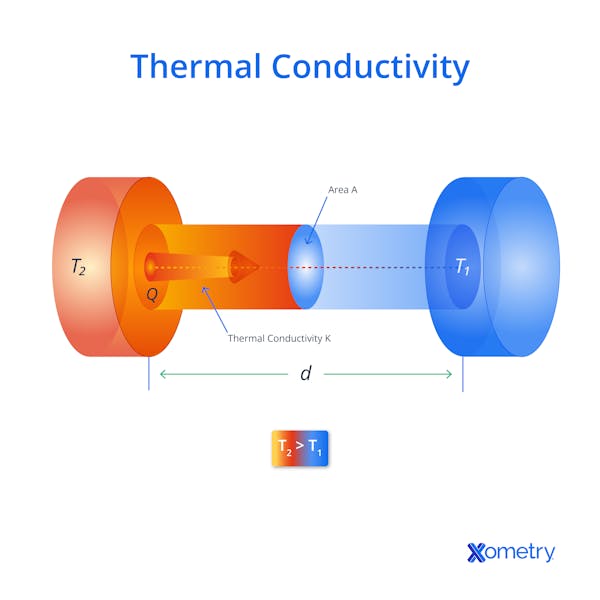
How Does Thermal Resistance Work?
A material's thermal resistance is a measure of how difficult it is for heat to pass through it. It is determined by the thermal conductivity and thickness of the material. Highly resistive materials, like insulators, slow the transfer of heat while those with low thermal resistance, like metals, facilitate it.
What Is the Importance of Thermal Resistance?
Thermal resistance is significant because it represents a material's or system's capacity to hinder the flow of heat. It is a key factor in the development and improvement of thermal management systems meant to avoid overheating and boost energy effectiveness.
What Is the Importance of Thermal Resistance in 3D Printing?
Thermal resistance is a critical part of a 3D printer’s design because it influences the melting and cooling of the print material, which in turn influences the final object's quality. Prints can be enhanced and errors avoided with proper thermal management and an understanding of thermal resistance.
What Is the Thermal Resistance of Different 3D Printing Materials?
The thermal resistance of some popular 3D printing materials can only be determined by calculating it using the formula below:
R = L / kA
To calculate the thermal resistance of an item, you first need to know the thickness of the material (L), its cross-sectional area perpendicular to the heat flow (A), and the material’s thermal conductivity (k).
Importance Thermal Resistance in Laser Cutting
Thermal resistance is important because it affects a material's capacity to withstand the high temperatures produced by the laser-cutting process. While materials with low thermal resistance may need to be cut slowly to avoid material damage, materials with high thermal resistance can be cut at higher speeds with little distortion or melting.
How Important Is Thermal Resistance in Plastic Injection Molding?
Thermal resistance is crucial to the process of plastic injection molding because it impacts the functionality and quality of the finished product. It calls attention to the material's capacity to withstand high temperatures without deteriorating or deforming. Plastic with the wrong thermal qualities may warp, crack, or lose its shape during the molding process, producing faulty products. It is important to choose a plastic material with the right thermal resistance to ensure consistent quality and production efficiency.
What Is the Formula for Thermal Resistance?
Here’s the technical bit. To calculate the thermal resistance in a material, you’ll first need to know the keys:
R = Thermal resistance (degrees Kelvin per watt (K/W) or Celsius per watt (°C/W))
L = Thickness of the material (m) perpendicular to the heat flow
k = Thermal conductivity (W/mK) (how well the material conducts heat)
A = Cross-sectional area perpendicular to heat flow (m²)
The thermal resistance of a flat object and some popular 3D printing materials can be determined by the following equation for steady-state heat transfer, which basically translates to “thermal resistance = thickness / (area x thermal conductivity):
R = L / kA
So, as you can see, to figure out the thermal resistance of a material, you’ll need to know its thickness, cross-sectional area, and thermal conductivity. Measuring the thickness and cross-sectional area is pretty straightforward and can be done with a ruler or caliper. You’ll need to refer to the Material Safety Data Sheet to find its thermal conductivity. Once you’ve got all that info, you can go ahead and do the equation.
The thermal resistance formula for conductive heat transfer is a rearranged version of Fourier’s Law of Heat Conduction:
Q = kAΔT / L
Q = Heat transfer rate (W)
ΔT = Temperature difference across the material (K or °C)

| Item | Thickness | Thermal conductivity | Area | Equation | Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Item Steel plate | Thickness 0.02 m | Thermal conductivity 50 W/mK | Area 0.5 m² | Equation R = 0.02 / 50 × 0.5 | Result 0.0008 K/W |
Item Copper pipe | Thickness 0.02 m | Thermal conductivity 401 W/mK | Area 0.1 m² | Equation R = 0.02 / 401 × 0.1 | Result 0.0005 K/W |
Item Glass window | Thickness 0.003 m | Thermal conductivity 0.8 W/mK | Area 2 m² | Equation R = 0.003 / 0.8 × 2 | Result 0.001875 K/W |
Thermal resistance calculation examples
Steel Plate
A steel plate with a thickness of 2 cm and a thermal conductivity of 50 W/mK has an area of 0.5 m².
Thermal resistance = thickness / (area x thermal conductivity)
Thermal resistance = 0.02 m / (0.5 m² x 50 W/mK)
Thermal resistance = 0.0008 K/W
Copper Pipe
A 2-meter pipe with a diameter of 10 cm and a thickness of 5 mm is made of copper, which has a thermal conductivity of 400 W/mK.
First, we need to calculate the area of the pipe's cylindrical surface:
Area = π x diameter x length
Area = π x 0.1 m x 2 m
Area = 0.628 m²
Then, we can use the thermal resistance formula:
Thermal resistance = thickness / (area x thermal conductivity)
Thermal resistance = 0.005 m / (0.628 m² x 400 W/mK)
Thermal resistance = 0.0000199 K/W
Glass Window
A window has a thickness of 3 mm and thermal conductivity of 0.8 W/mK. The window has an area of 2 m².
Thermal resistance = thickness / (area x thermal conductivity)
Thermal resistance = 0.003 m / (2 m² x 0.8 W/mK)
Thermal resistance = 0.001875 K/W
Make sure the thickness, area, and thermal conductivity are all expressed in the same unit of measurement (e.g., all in meters or all in inches) and that the units cancel out properly in the formula.
What Are the Factors That Affect the Thermal Resistance of Materials?
Several factors affect the thermal resistance of a material, including:
1. Pressure
By changing a material's thermal conductivity (capacity to transfer heat), pressure can have an impact on thermal resistance. Higher pressure results in lower thermal conductivity and, consequently, higher thermal resistance.
2. Surface Area
Surface area influences the rate of heat transfer between the material and its surroundings and thus affects the thermal resistance of materials. The part can be made more effective at transferring heat by increasing surface area and lowering thermal resistance.
3. Porosity
One of the elements that affect a material's ability to resist heat is its porosity. The air within the pores transfers heat convectively, making a porous item’s thermal conductivity different from that of a non-porous version of the same material. Particularly for materials used as insulation, where high thermal resistance is desired, this difference in thermal resistance may be significant.
4. Material Composition
The chemical makeup of a material is known as its composition. This has a large influence on the material's capacity to conduct heat. Parts made with materials with poor thermal conductivity typically have a high thermal resistance. A material's composition thus has a direct impact on its thermal resistance.
5. Temperature Difference
Temperature difference affects thermal resistance because its tendency to transfer heat depends on the temperature difference between one surface and the other.
6. Material Thickness
A material's thermal resistance rises along with its thickness because there is more material for heat to pass through. Thicker materials generally resist heat transfer better than thin ones. Nevertheless, the precise relationship between thickness and thermal resistance depends on the characteristics of the material and the mode of heat transfer.
What Are the Benefits of Thermal Resistance?
High thermal resistance can be valuable for several reasons:
- Energy Efficiency: Thermally resistant insulation helps lower the amount of energy required to maintain a proper temperature in a building or other enclosed space by restricting the flow of heat. That can lower energy costs and give the building a smaller carbon footprint.
- Temperature Control: Thermal resistance can help maintain a steady temperature in an enclosed area. It makes the space more comfortable for its occupants and less likely to cause damage to machinery or other contents that may be sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
- Fire Protection: High-thermal-resistance materials can slow the spread of fire, giving occupants more time to flee and minimizing property damage.
What Are the Limitations of Thermal Resistance?
Listed below are some of the imperfections regarding thermal resistance:
- Limited Effectiveness: High thermal resistance materials can reduce the speed of heat transfer, but they cannot completely prevent it. No matter how resistant a material is, heat will always travel from warmer to cooler regions.
- Moisture /issues: Many materials gradually absorb moisture. This is true of some materials with high thermal resistance such as fiberglass insulation. It may also result in problems like mold growth and a reduction in their insulating effectiveness.
- Insufficient /insulation: In some circumstances, even excellent insulation might not be sufficient to stop heat gain or loss in a building or other enclosed space. Temperature variations may also be caused by other factors such as air leakage and inadequate ventilation.
What Are Examples of Thermal Resistance of Different Materials?
To determine the thermal resistance of an item, you will need to determine its area, thickness, and thermal conductivity first. Once you know these values, compute its thermal resistance using the following formula below:
R = L / kA
For example: Consider that we have two flat plates, one made of steel and the other of copper. Both plates have a 0.02-meter thickness and a 0.1 m2 cross-sectional area.
The thermal conductivity of copper is approximately 401 W/mK, while the thermal conductivity of steel is approximately 50 W/mK.
Using the formula R = L / kA, we can calculate the thermal resistance of each plate:
For the copper plate:
R = 0.02 m / (401 W/mK * 0.1 m^2)
R = 0.0005 K/W
For the steel plate:
R = 0.02 m / (50 W/mK * 0.1 m^2)
R = 0.004 K/W
The copper plate has significantly less thermal resistance than the steel plate, which means it will conduct heat more effectively.
What Does High Thermal Resistance Mean?
A material with high thermal resistance does not easily allow heat energy to travel through its thickness. This property is crucial in industries like electronics or aerospace where heat management is fundamental.
Does Higher Resistance Mean More Heat?
No, increased thermal resistance does not equate to increased heat. The capacity of a material to withstand the transfer of heat is referred to as thermal resistance. Although a material with greater thermal resistance slows the transfer of heat, it says nothing about the absolute amount of heat in total. Additionally, other elements like temperature difference and surface size affect how much heat is produced or transferred.
Does High Resistance Increase Heat?
No, high thermal resistance does not increase heat. Items of high thermal resistance obstruct the movement of heat between two surfaces. This is why materials with high thermal resistance, like insulation, are frequently used to impede heat transfer and keep internal temperatures stable.
Does High Resistance Increase Temperature?
No, a high thermal resistance does not raise the temperature. Thermal resistance is a measure of the substance’s tendency to withstand the flow of heat. High-thermal-resistance materials will stop heat from moving quickly, but they won't raise the temperature on their own.
What Material Has Highest Thermal Resistance?
Tantalum carbide has the ability to withstand extremely high temperatures, almost reaching 4000 °C, making it known as the material with the highest thermal resistance in the world. Due to its exceptional heat resistance, it has found use in many industrial applications, including as a ceramic reinforcement in high-entropy alloys (HEAs) and a sintering additive for ultra-high temperature ceramics (UHTCs).
What Does Low Thermal Resistance Mean?
Low thermal resistance is a descriptor for items that allow heat energy to easily pass through or across them. A material or structure that has a low thermal resistance is likely to be a good heat conductor, enabling heat to move through it quickly and easily. Many electronic devices, for instance, need to enhance heat transfer away from hot components in order to optimize their performance. They use conductive materials with low thermal resistance to do so.
What Material Has Lowest Thermal Resistance?
Graphene, an effectively two-dimensional material made of a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, is currently thought to have the lowest thermal resistance in the world. Though largely experimental thus far, graphene shows promise for applications that need, particularly speedy heat transfer.
Is Higher or Lower Thermal Resistance Better?
Both situations have their uses. Insulating materials need to exhibit high thermal resistance to slow heat infiltration or exfiltration from insulated regions. On the flip side, devices like radiators need to be made of materials with low thermal resistance because their purpose is to transfer heat away from themselves and their associated devices.
What Is the Difference Between Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Resistance
Thermal resistance describes how well (or not) a particular material can resist heat flow, and thermal conductivity measures a material's inherent capacity to conduct heat.
How Xometry Can Help
Any questions on thermal resistance? Get in touch with one of our representatives, who can answer all your queries and guide you in the right direction. You can also quickly and easily get an estimate for any of our many prototyping and production services—get started today by uploading your designs to the Xometry Instant Quoting Engine®!
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


