Arc and gas welding are both methods that use intense heat to join metal components by melting them and allowing them to fuse upon cooling. The main difference between the two is the way the heat is generated. Arc welding uses electricity to generate a much higher temperature. Gas welding creates a slightly lower temperature by burning gases (most commonly acetylene) with oxygen to generate a flame that melts the metal to be welded. This article will further compare arc welding vs. gas welding.
What Is Arc Welding?
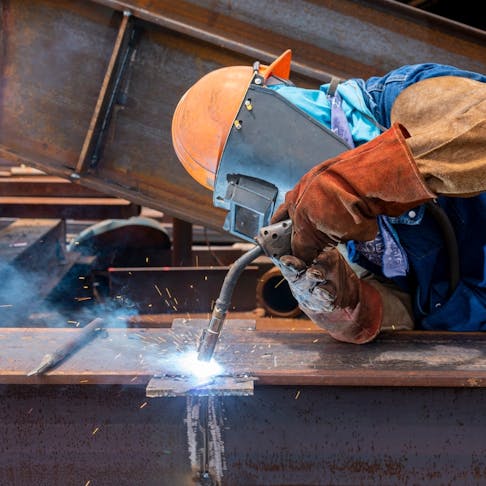
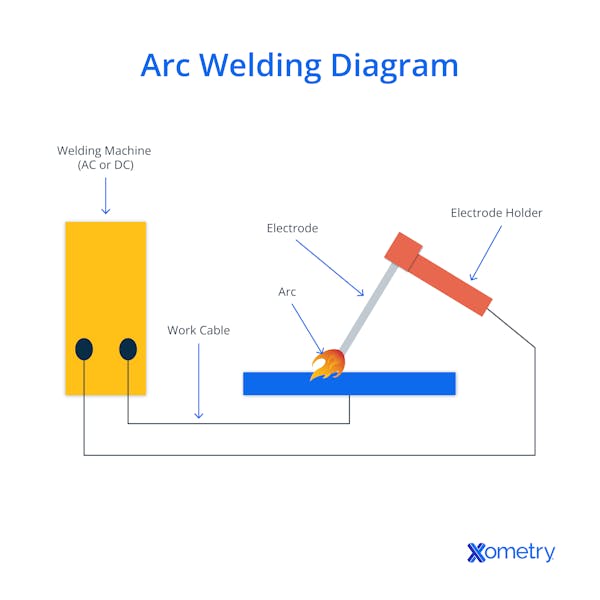
Arc welding is a process that uses the heat of an arc to join metal materials together. The arc—generated by electricity—melts the metal at the joint under the intense heat of approximately 6,500°F. The molten metals then fuse together upon cooling.
A suitable filler metal is continuously supplied to assist in the joining of the metal workpieces. This filler, which becomes molten at the site of the weld pool, solidifies along with the workpiece metal upon cooling, creating a metallurgical bond.
Arc welding includes several subtypes, the most common of which are Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Metal Inert Gas (MIG), and Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding. While this article compares arc welding broadly with gas welding, it's worth noting that TIG and MIG welding are widely used in industrial applications due to their precision and speed, respectively. For more information, see our guide on Arc Welding.
How Does Arc Welding Work?
Arc welding works by creating an electric arc to generate heat. This is achieved by attaching a grounding wire to a metal structure and a ground clamp to the workpiece and using an electrode to strike an arc at the welding joint. Once the electrode lead touches the material to be welded, an electric arc is created that produces a bright white light and sparks.
The resistance to the flow of electrons across the air gap is what produces the intense heat that melts the metal material and filler material (sometimes referred to as the welding rod). The resultant pool of metal then solidifies and fuses the edges of the original material to join the metal together. Molten metal may react with oxygen and nitrogen in the air, potentially weakening the weld. To prevent this, shielding gas or flux is used to protect the weld pool.
What Is the Purpose of Arc Welding?
The purpose of arc welding is to join two pieces of metal together using electricity. This is done by creating an electric arc that melts the metal at the joint, allowing both pieces to fuse together upon cooling. Upon cooling, the two metals are joined. By fusing the materials together in this way, arc welding ensures the bond between the metals is incredibly strong and sustainable.
What Are the Uses of Arc Welding?
Arc welding is used to join different materials together in a range of industries. One example is in the construction industry, in which arc welding is used to guarantee robust, durable, and secure connections between metals that support infrastructure such as buildings, bridges, and other forms of construction. It is also used in the aerospace industry to repair and manufacture parts for aircraft as well as join sheeting. Another example is heavy equipment repair and pipeline welding in the construction industry. Other examples include the automotive, shipbuilding, oil, gas, and power industries.
What Type of Laser Is Used in Arc Welding?
In normal arc welding, there are no lasers used. Instead, an arc is produced using an electrode that locally melts the metal of the two workpiece sections. This is achieved by a grounding wire that attaches to a metal surface, and an electrode lead placed on the material to be welded. Once the electrode touches the material to be welded, an electric arc is created that generates heat to create a weld.
What Are the Advantages of Arc Welding?
Listed below are the advantages of arc welding:
- Low Equipment Cost: Less equipment is needed as the process uses electricity, rather than gas, to generate heat. AC or DC electric current can be used to produce this heat. The equipment that is necessary to carry out this form of welding is affordable and can be maintained at a relatively low cost.
- Portable: Less equipment needed means it is easily transportable.
- Results in Acceptable Appearance: Arc welding can be used on less-than-clean metals and, in skilled hands, can produce reasonably clean welds. However, it may generate noticeable spatter and distortion depending on the material and process used.
- Strong Bond: Arc welding produces strong bonds between the two materials that have been welded together.
What Are the Disadvantages of Arc Welding?
Listed below are the disadvantages of arc welding:
- Moderate Efficiency: Arc welding can produce slag and spatter, which may result in material waste and require post-weld cleanup. It may not be the most efficient choice for continuous or precision welding tasks.
- High Level of Skill Needed: The level of skill required by operators to guide the arc is extremely high. A lot of training is needed for professionals to be able to carry out this process, which can be costly.
- Limited Material Compatibility: Arc welding is not suitable for all types of metals, especially certain reactive or thin materials, which may require more specialized welding methods.
What Is Gas Welding?
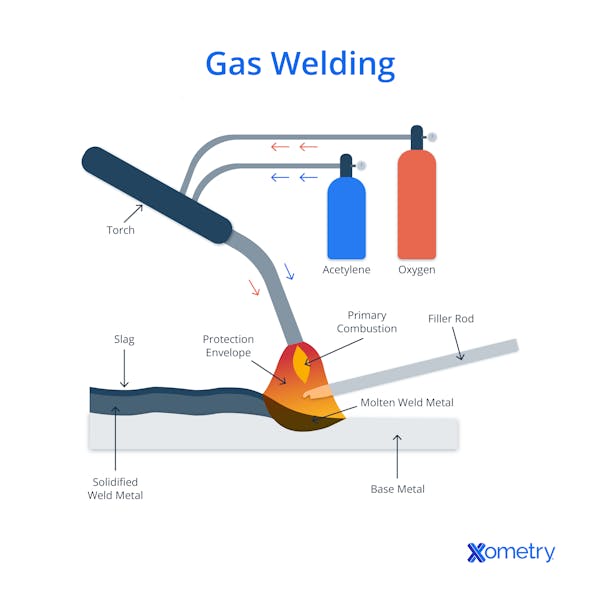
Gas welding is one of the oldest types of fusion welding that uses a flame to generate heat. Similar to arc welding, gas welding joins metals together by heating the metal which then fuses together upon cooling. However, the heat necessary for gas welding is produced by burning a combination of different gases rather than by an electric arc.
How Does Gas Welding Work?
Gas welding works by using the heat generated from burning gases to then cut and/or fuse metals together. Fuel gas (stored in a fuel cylinder), such as acetylene, is mixed with oxygen (from a separate oxygen cylinder) and burnt to produce a concentrated flame that can reach temperatures of around 5,700°F. Both gases have individual control valves to regulate the oxygen ratio within a mixer chamber. The equipment from which the flame ultimately emerges is the welding torch. The flame is then used to locally melt the surface of the metals, which then fuse together along with molten filler metal from a suitable rod.
What Is the Purpose of Gas Welding?
The purpose of gas welding is to fuse materials together under a flame that is produced by burning gases such as acetylene. By fusing materials together in this way, there is no requirement for the use of electricity. Gas welding can be used to join both non-ferrous and ferrous materials, especially in thin sections.
What Are the Uses of Gas Welding?
Gas welding is used in a range of scenarios but is very suitable for welding pipes and tubes. Gas welding was traditionally used in the construction and repair of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, though it has been largely replaced by modern welding techniques in many of these applications. Other examples include light fabrication tasks such as welding gas bottles, hot water pipes, boilers, and some types of repair work, though it is rarely used in high-precision or high-pressure applications like nuclear heat exchangers today.
What Type of Laser is Used in Gas Welding?
Lasers are not used in traditional gas welding. Instead, the heat is generated by burning gases to produce a flame which is then concentrated on the metals to be fused.
What Are the Advantages of Gas Welding?
Listed below are the advantages of gas welding:
- Ease of Use: Compared to many other welding methods, gas welding is relatively simple and can be performed with basic training, making it accessible for small-scale or field repairs.
- Portability: Gas welding equipment does not require electricity, making it suitable for use in remote locations. The equipment is generally lightweight, self-contained, and more affordable than many electric welding systems.
What Are the Disadvantages of Gas Welding?
The disadvantages of gas welding are listed below:
- Lower Temperature: Gas welding produces flame temperatures around 5,700°F, which is lower than the 6,500°F achieved by arc welding. This makes it less suitable for welding thick or high-strength steel sections.
- Requires Post-Welding Finish: Gas welding typically results in a rougher surface finish and more oxidation than other methods, so additional finishing work may be needed for aesthetic or functional purposes.
How To Choose Between Arc Welding and Gas Welding?
The choice between arc welding and gas welding depends on the application and the part output requirement. For example, when welding together thick materials, arc welding is a much better option. As electricity can generate a much higher temperature, arc welding can cut through and join thicker metals, whereas gas welding cannot. However, gas welding is often preferred for thin metals like sheet metal because it provides more control and less risk of burn-through. Some arc welding methods can also be used on thin materials but require more skill and control. If cost is the primary concern, gas welding is often the more affordable option since it does not require electricity.
Which Welding Method Is Faster — Arc Welding or Gas Welding?
Arc welding is generally faster than gas welding, especially for thicker materials, due to its higher heat input and deeper penetration. There is a much higher temperature in arc welding vs. gas welding. The extreme heat generated by the electric arc means the process is more efficient at melting metal and provides quicker heating times. This also means there is less distortion in the metals themselves.
How Does the Heat Source Differ Between Arc Welding and Gas Welding?
The heat source in arc welding is produced by electricity, which generates enough heat to melt metals and fuse them together. In gas welding, the heat is produced by burning a gas such as acetylene mixed with oxygen to generate a flame which then melts the metal. The difference between these two heat sources means that the resultant heat generated is slightly different. Arc welding can reach much higher temperatures than gas welding. Arc welding typically does not require preheating for many common applications. In contrast, gas welding often benefits from preheating the metal to ensure consistent fusion, particularly with thicker or dissimilar metals.
Which Method Is Better for Welding Steel And Iron — Arc Welding or Gas Welding?
Both arc welding and gas welding can be used to weld steel and iron. However, gas welding can weld much thinner sheet metal than arc welding. Arc welding is much more efficient and economical over an extended period of time, and it can also create stronger welds.
Which Welding Procedure Is Better Suited for Portability?
Gas welding is slightly better suited for portability, despite arc welding also being well suited for portability. Gas welding only requires fuel and oxygen cylinders along with a torch, making it convenient for locations without electrical power. However, with the arc welding procedure, an electricity source is required to generate the heat.
Which Welding Method Is Riskier Regarding Fuel Gases and Oxygen?
Both arc welding and gas welding are inherently dangerous activities. Arc welding has the potential to burn your skin, electrocute you, burn your retinas, damage hearing, and create carcinogenic fumes. The gas used for gas welding is flammable/explosive when mixed with oxygen or air in certain ratios, so leaks are extremely dangerous. Gas welding carries risks, including burns, eye damage from bright flames, and the potential release of toxic fumes. Additionally, the use of flammable gases increases the risk of fire or explosion if not properly handled. Both forms of welding are inherently dangerous, however, the risk is mitigated to appropriate levels with proper training and the use of personal protective equipment.
Does Gas Welding Produce Stronger and More Durable Welds Than Arc Welding?
No, arc welding typically produces stronger and more durable welds than gas welding, especially on thicker or structural metals. The quality of the weld can be dependent on the welder’s skill and the temperature generated. Since arc welding produces a much higher temperature to create the welds, there is deeper penetration, which creates better fusing of metals and, subsequently, less distortion of the materials overall.
Does Gas Welding Equipment Typically Cost Less Than Arc Welding Equipment?
Yes, gas welding has a relatively cheap initial capital outlay. There are higher upfront costs with arc welding for the equipment needed, and, of course, electricity is required. However, in the long run, the difference between arc welding and gas welding is that arc welding is much more efficient and can weld materials far quicker. The consistency and precision of arc welding cuts down on cost by preventing the need to grind out and re-weld. Additionally, the cost of purchasing welding gases combined with the maintenance of the gas welding bottles and torches doesn’t necessarily make it the cheaper option.
Can Arc Welding Be Used for Joining Lighter Metals Such as Aluminum?
Yes, arc welding can be used to join lighter metals like aluminum, though it is more technically challenging and often requires specific techniques such as TIG or MIG welding. Steel is the most common metal used in arc welding, and in comparison, aluminum is much harder. As aluminum is an active metal, it is much more challenging to create a binding filler to weld aluminum with. Additionally, aluminum has a high heat conductivity and a low melting point, which makes it hard not to melt the pieces involved. However, arc welding can be used to join aluminum alloy series types such as 1xxx, 3xxx, 5xxx, and 6xxx.
Summary
This article presented arc welding vs. gas welding, explained each of them, and discussed their differences. To learn more about both arc welding and gas welding, contact a Xometry representative.
Xometry provides a wide range of manufacturing capabilities, including casting and other value-added services for all of your prototyping and production needs. Visit our website to learn more or to request a free, no-obligation quote.
Disclaimer
The content appearing on this webpage is for informational purposes only. Xometry makes no representation or warranty of any kind, be it expressed or implied, as to the accuracy, completeness, or validity of the information. Any performance parameters, geometric tolerances, specific design features, quality and types of materials, or processes should not be inferred to represent what will be delivered by third-party suppliers or manufacturers through Xometry’s network. Buyers seeking quotes for parts are responsible for defining the specific requirements for those parts. Please refer to our terms and conditions for more information.


